- 问题展现
-
解决代码
-
代码1
- 输出结果
-
代码2
- 输出结果
-
代码3
- 输出结果
-
代码1
问题展现
假设有一个旅行商人要拜访全国 31 个省会城市,他需要选择所要走的路径,路径的限制是每个城市只能拜访一次,而且最后要回到原来出发的城市。路径的选择要求是:所选路径的路程为所有路径之中的最小值。
全国 31 个省会城市的坐标为 [1304 2312; 3639 1315; 4177 2244; 3712 1399; 3488 1535; 3326 1556; 3238 1229; 4196 1004; 4312 790; 4386 570; 3007 1970; 2562 1756; 2788 1491; 2381 1676; 1332 695; 3715 1678; 3918 2179; 4061 2370; 3780 2212; 3676 2578; 4029 2838; 4263 2931; 3429 1908; 3507 2367; 3394 2643; 3439 3201; 2935 3240; 3140 3550; 2545 2357; 2778 2826; 2370 2975]。
解决代码
代码1
clc; close all; clear
% 设置初始化参数
NC_max=200; % 最大迭代次数
m=50; % 蚂蚁个数
Alpha=1; % 表征信息素重要程度的参数
Beta=5; % 表征启发式因子重要程度的参数
Rho=0.1;% 信息素蒸发系数
Q=100;% 信息素增加强度系数
% n个城市的坐标,n×2的矩阵
Citys = [1304 2312;3639 1315;4177 2244;3712 1399;3488 1535;3326 1556;...
3238 1229;4196 1044;4312 790;4386 570;3007 1970;2562 1756;...
2788 1491;2381 1676;1332 695;3715 1678;3918 2179;4061 2370;...
3780 2212;3676 2578;4029 2838;4263 2931;3429 1908;3507 2376;...
3394 2643;3439 3201;2935 3240;3140 3550;2545 2357;2778 2826;...
2370 2975];
%% 第1步:变量初始化
n = size(Citys, 1); % n表示问题的规模(城市个数)
D = distanceMatrix(Citys); % D表示完全图的赋权邻接矩阵
Eta = 1 ./ D; % Eta为启发因子,这里设为距离的倒数
Tau = ones(n, n); % Tau为信息素矩阵
Tabu = zeros(m, n); % 存储并记录路径的生成
NC = 1; % 迭代计数器,记录迭代次数
R_best = zeros(NC_max, n); % 各代最佳路线
L_best = inf .* ones(NC_max, 1); % 各代最佳路线的长度
L_ave = zeros(NC_max, 1); % 各代路线的平均长度
while NC <= NC_max % 停止条件之一:达到最大迭代次数,停止
%% 第2步:将m只蚂蚁放到n个城市上
Randpos = []; % 随机存取
for i = 1:(ceil(m / n))
Randpos = [Randpos, randperm(n)];
end
Tabu(:, 1) = (Randpos(1, 1:m))';
%% 第3步:m只蚂蚁按概率函数选择下一座城市,完成各自的周游
for j=2:n % 所在城市不计算
for i=1:m
visited=Tabu(i,1:(j-1)); % 记录已访问的城市,避免重复访问
J = 1:n; % 待访问的城市
J(ismember(J, visited)) = []; % 删除已访问城市
% 计算待选城市的概率分布
P = (Tau(visited(end), J).^Alpha) .* (Eta(visited(end), J).^Beta);
% visited(end)表示蚂蚁现在所在城市编号,J(k)表示下一步要访问的城市编号
P=P/(sum(P)); % 把各个路径概率统一到和为1
% 按概率原则选取下一个城市
Pcum=cumsum(P); % cumsum,元素累加即求和
% 蚂蚁要选择的下一个城市不是按最大概率,就是要用到轮盘法则,不然影响全局收缩能力,所以用累积函数
Select=find(Pcum>=rand); % 若计算的概率大于原来的就选择这条路线
to_visit=J(Select(1));
Tabu(i,j)=to_visit; % 提取这些城市的编号到to_visit中
end
end
% 将当前最佳路径加入到下一次迭代
if NC >= 2
Tabu(1,:) = R_best(NC-1,:);
end
%% 第4步:记录本次迭代最佳路线
L = zeros(m, 1); % 开始距离为0,m*1的列向量
for i = 1:m
R = Tabu(i, :);
for j = 1:(n - 1)
L(i) = L(i) + D(R(j), R(j + 1)); % 原距离加上第j个城市到第j+1个城市的距离
end
L(i) = L(i) + D(R(1), R(n)); % 一轮下来后走过的距离
end
L_best(NC) = min(L); % 最佳距离取最小
pos = find(L == L_best(NC));
R_best(NC, :) = Tabu(pos(1), :); % 此轮迭代后的最佳路线
% 找到路径最短的那条蚂蚁所在的城市先后顺序
% pos(1)中1表示万一有长度一样的两条蚂蚁,那就选第一个
L_ave(NC) = mean(L); % 此轮迭代后的平均距离
NC = NC + 1; % 迭代继续
%% 第5步:更新信息素
Delta_Tau = zeros(n, n); % 开始时信息素为n*n的0矩阵
for i = 1:m
R = Tabu(i, [1:n, 1]);
indices = sub2ind(size(Delta_Tau), R(1:end-1), R(2:end));
Delta_Tau(indices) = Delta_Tau(indices) + Q ./ L(i);
end % 此次循环在路径(i,j)上的信息素增量
Tau = (1 - Rho) .* Tau + Delta_Tau;
%% 第6步:禁忌表清零
Tabu = zeros(m, n); % 直到最大迭代次数
end
%% 第7步:输出结果
Pos = find(L_best == min(L_best));
Shortest_Route = R_best(Pos(1), :);
Shortest_Length = L_best(Pos(1));
displayResults(Citys, Shortest_Route, Shortest_Length, L_best, L_ave)
disp(['最短距离:' num2str(Shortest_Length)]);
disp(['最短路径:' num2str([Shortest_Route Shortest_Route(1)])]);
%% 函数部分
function D = distanceMatrix(C)
n = size(C, 1);
D = zeros(n, n);
for i = 1:n
for j = 1:n
if i ~= j
D(i, j) = norm(C(i, :) - C(j, :));
else
D(i, j) = eps;
end
D(j, i) = D(i, j);
end
end
end
function displayResults(Citys, Shortest_Route, Shortest_Length, L_best, L_ave)
figure(1)
N = length(Shortest_Route);
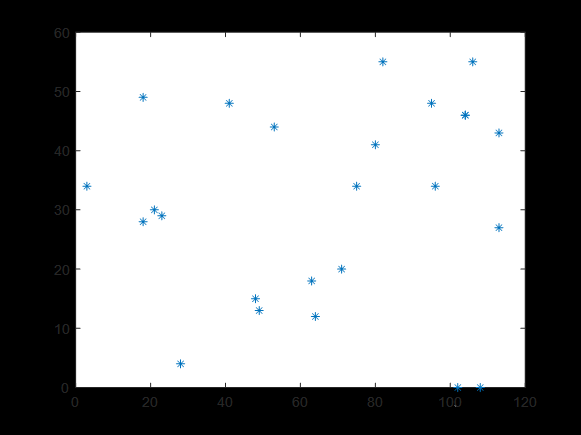
scatter(Citys(:, 1), Citys(:, 2));
hold on;
R = [Shortest_Route, Shortest_Route(1)];
for ii = 1:N
plot(Citys(R(ii:ii+1), 1), Citys(R(ii:ii+1), 2),'o-', 'LineWidth',1.5);
hold on;
end
text(Citys(Shortest_Route(1), 1), Citys(Shortest_Route(1), 2), ' 起点');
text(Citys(Shortest_Route(end), 1), Citys(Shortest_Route(end), 2), ' 终点');
xlabel('城市位置横坐标');
ylabel('城市位置纵坐标');
title('蚁群算法优化旅行商问题');
grid on;
figure(2)
plot(1:length(L_best), L_best(1:end), 'b', 'LineWidth',1.5);
hold on;
plot(1:length(L_ave), L_ave(1:end), 'r', 'LineWidth',1.5);
legend('最短距离', '平均距离');
xlabel('迭代次数');
ylabel('距离');
title('平均距离和最短距离');
end
输出结果
最短距离:15609.4771
最短路径:15 14 12 13 11 23 16 5 6 7 2 4 8 9 10 3 18 17 19 24 25 20 21 22 26 28 27 30 31 29 1 15

 文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-414257.html
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-414257.html
代码2
clc; close all; clear
% Initialize the parameters
num_ants = 50; % Number of ants
num_iterations = 200; % Number of iterations
alpha = 1; % Importance of pheromone
beta = 5; % Importance of heuristic information
rho = 0.1; % Evaporation rate of pheromone
coordinates = [1304 2312;3639 1315;4177 2244;3712 1399;3488 1535;3326 1556;...
3238 1229;4196 1044;4312 790;4386 570;3007 1970;2562 1756;...
2788 1491;2381 1676;1332 695;3715 1678;3918 2179;4061 2370;...
3780 2212;3676 2578;4029 2838;4263 2931;3429 1908;3507 2376;...
3394 2643;3439 3201;2935 3240;3140 3550;2545 2357;2778 2826;...
2370 2975];
% Calculate distance matrix
n = size(coordinates, 1);
dist_matrix = zeros(n);
% error statement!!!
% start_city_custom = input(sprintf('Enter the starting city index (1 to %d): ', n));
% start_city = start_city_custom;
for i = 1:n
for j = i+1:n
dist_matrix(i, j) = norm(coordinates(i, :) - coordinates(j, :));
dist_matrix(j, i) = dist_matrix(i, j);
end
end
% Initialize the pheromone matrix
pheromone = ones(n, n);
% Start the iterations
best_distance = inf;
best_path = [];
for i = 1:num_iterations
paths = zeros(num_ants, n + 1);
path_lengths = zeros(num_ants, 1);
% For each ant
for j = 1:num_ants
start_city = randi(n);
paths(j, 1) = start_city;
for step = 2:n
current_city = paths(j, step - 1);
not_visited = setdiff(1:n, paths(j, 1:step - 1));
prob = (pheromone(current_city, not_visited) .^ alpha) .* ((1 ./ dist_matrix(current_city, not_visited)) .^ beta);
probabilities = prob / sum(prob);
next_city = not_visited(randsample(length(not_visited), 1, true, probabilities));
paths(j, step) = next_city;
end
paths(j, n + 1) = paths(j, 1);
path_lengths(j) = sum(dist_matrix(sub2ind(size(dist_matrix), paths(j, 1:n), paths(j, 2:n + 1))));
if path_lengths(j) < best_distance
best_distance = path_lengths(j);
best_path = paths(j, :);
end
end
% Update the pheromone matrix
pheromone = (1 - rho) * pheromone;
for j = 1:num_ants
for step = 1:n
pheromone(paths(j, step), paths(j, step + 1)) = ...
pheromone(paths(j, step), paths(j, step + 1)) + 1 / path_lengths(j);
end
end
end
% Print the best path
num_cities = size(coordinates, 1);
fprintf('Optimal path:\n');
for j = 1:num_cities
fprintf('%d -> ', best_path(j));
end
fprintf('%d\n', best_path(1));
fprintf('Optimal distance: %f\n', best_distance);
% {
% start_city=randi(n)用于为每只蚂蚁随机选择起始城市。
% n 代表城市数,randi(n) 生成1到n(含)之间的随机整数。
% 蚂蚁从不同的城市开始,这增加了探索解决方案的多样性,有助于防止算法陷入局部最优。
% }
输出结果
Optimal path:
14 -> 12 -> 13 -> 11 -> 23 -> 16 -> 5 -> 6 -> 7 -> 2 -> 4 -> 8 -> 9 -> 10 -> 3 -> 18 -> 17 -> 19 -> 24 -> 25 -> 20 -> 21 -> 22 -> 26 -> 28 -> 27 -> 30 -> 31 -> 29 -> 1 -> 15 -> 14
Optimal distance: 15609.477144
代码3
clc; close all; clear
% Coordinates of 31 provincial capital cities in China
coords = [1304 2312;3639 1315;4177 2244;3712 1399;3488 1535;3326 1556;...
3238 1229;4196 1044;4312 790;4386 570;3007 1970;2562 1756;...
2788 1491;2381 1676;1332 695;3715 1678;3918 2179;4061 2370;...
3780 2212;3676 2578;4029 2838;4263 2931;3429 1908;3507 2376;...
3394 2643;3439 3201;2935 3240;3140 3550;2545 2357;2778 2826;...
2370 2975];
% Calculate distance matrix
n = size(coords, 1);
dist_matrix = zeros(n);
for i = 1:n
for j = i+1:n
dist_matrix(i, j) = norm(coords(i, :) - coords(j, :));
dist_matrix(j, i) = dist_matrix(i, j);
end
end
% Initialize ACO parameters
n_ants = 50;
n_iterations = 200;
alpha = 1;
beta = 5;
rho = 0.1;
Q = 100;
% ACO algorithm
[best_path, best_dist, avg_dists, best_dists] = ACO(dist_matrix, n_ants, n_iterations, alpha, beta, rho, Q);
% Display the optimal path and its distance
disp("Optimal path:");
optimal_path_str = join(string(best_path), "->");
disp(optimal_path_str);
disp("Optimal distance:");
% disp(best_dist);
fprintf('%.6f\n', best_dist);
% Plot the cities and the optimal path
figure;
plot(coords(:, 1), coords(:, 2), 'o');
hold on;
plot(coords(best_path, 1), coords(best_path, 2), '-');
title('Cities and the Optimal Path');
xlabel('X Coordinate');
ylabel('Y Coordinate');
grid on;
% Annotate city numbers
for i = 1:n
text(coords(i, 1), coords(i, 2), num2str(i), 'HorizontalAlignment', 'left', 'VerticalAlignment', 'bottom');
end
% Plot the convergence curves
figure;
plot(1:n_iterations, best_dists, 'b-', 1:n_iterations, avg_dists, 'r-');
title('Convergence Curves');
xlabel('Number of Iterations');
ylabel('Path Distance');
legend('Best Path', 'Average Path');
grid on;
% ACO function
function [best_path, best_dist, avg_dists, best_dists] =...
ACO(dist_matrix, n_ants, n_iterations, alpha, beta, rho, Q)
n = size(dist_matrix, 1);
best_path = zeros(1, n + 1);
best_dist = Inf;
avg_dists = zeros(1, n_iterations);
best_dists = zeros(1, n_iterations);
pheromone_matrix = ones(n, n);
visibility_matrix = 1 ./ dist_matrix;
for iter = 1:n_iterations
paths = zeros(n_ants, n + 1);
path_lengths = zeros(n_ants, 1);
for ant = 1:n_ants
start_city = randi(n);
paths(ant, 1) = start_city;
for step = 2:n
current_city = paths(ant, step - 1);
not_visited = setdiff(1:n, paths(ant, 1:step - 1));
prob = (pheromone_matrix(current_city, not_visited) .^ alpha) .*...
(visibility_matrix(current_city, not_visited) .^ beta);
next_city = not_visited(randsample(length(not_visited), 1, true, prob / sum(prob)));
paths(ant, step) = next_city;
end
paths(ant, n + 1) = paths(ant, 1);
path_lengths(ant) = sum(dist_matrix(sub2ind(size(dist_matrix), paths(ant, 1:n), paths(ant, 2:n + 1))));
if path_lengths(ant) < best_dist
best_dist = path_lengths(ant);
best_path = paths(ant, :);
end
end
% Update pheromone matrix
pheromone_matrix = (1 - rho) * pheromone_matrix;
for ant = 1:n_ants
for step = 1:n
pheromone_matrix(paths(ant, step), paths(ant, step + 1)) = ...
pheromone_matrix(paths(ant, step), paths(ant, step + 1)) + Q / path_lengths(ant);
end
end
% Calculate average path length and record the best distance
avg_dists(iter) = mean(path_lengths);
best_dists(iter) = best_dist;
end
end
输出结果
Optimal path:
15->14->12->13->11->23->16->5->6->7->2->4->8->9->10->3->18->17->19->24->25->20->21->22->26->28->27->30->31->29->1->15
Optimal distance:
15609.477144

 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-414257.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-414257.html
到了这里,关于Matlab蚁群算法求解旅行商问题的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!