前言
学习一门语言,我们从熟悉其语法开始,慢慢深入动手实践,并开始将其使用到对应的场景上,当我们遇到相应的问题,能够联想到使用该技术,并能够信手拈来的时候,才是我们真正掌握了一门技术或者语言的时候。学习的时候可以和其他学过的知识点相关联,如ES可以与MYSQL特性相关联,就像编程入门从C开始一样,是介于C的语法基础,触类旁通其他语言,下面介绍的是ES的使用场景,语法,和对应的操作过程。
一. ES数据库说明
es数据库是一个搜索引擎,既可以存储数据,又可以将数据进行细粒度划分,切分为多个索引条件,并支持全文检索,是一个分布式概念的数据存储搜索引擎。基于JAVA和Lucence创建。
二. ES的常见概念
集群,节点,索引,类型,映射,文档,段域,反向索引,DSL索引
- 集群: 多个服务构建成一个集群
- 节点: 一个集群上的节点,指代集群上的一个服务
- 索引: index ,是es的一个基本概念,依靠索引可以进行数据的检索,相当于myql的数据库(database)的量级
- 映射: 在存储数据的时候规定映射规则可以限制存储进es的数据,相当于mysql的表结构。
- 文档:文档是es存储的基本单位,相当于mysql的行的概念
- 段域:相当于mysql的列
- 反向索引:相当于mysql正向查询
- DSL索引:依靠es查询规则而进行的查询,相当于mysql的sql查询
| ES | 关系型数据库 |
| 索引(index) | 数据库(DataBase) |
| 类型(Type) | 表(Table) |
| 映射(Mapping) | 表结构(Schema) |
| 文档(Document) | 行(ROw) |
| 字段(Field) | 列(Column) |
| 反向索引 | 正向索引 |
| DSL查询 | SQL查询 |
三. ES的应用场景
① 监控。对日志类数据进行存储、分析、可视化。对日志数据,ES给出了ELK的解决方案。其中logstash采集日志,ES进行复杂的数据分析,转换你的日志,并将他们存储在es中,kibana进行可视化展示。
② 线上商城系统,用户需要搜素购物系统网站上的商品信息。es可以存储所有的商品信息和一些库存信息,用户通过搜索引擎可以查询到自己需要的商品信息。
③ json文档数据库。用于存放java格式的文档。
④ 提供全文搜素并高亮关键字
四. ES的使用原理
存储和查询原理
lucence的存储和查询过程主要是:
存储过程:
① 存储文档经过词法分析得到一系列的词(Term)
② 通过一系列词来创建形成词典和反向索引表
③ 将索引进行存储并写入硬盘。
查询过程:
① 用户输入查询语句。
② 对查询语句经过词法分析得到一系列词(Term) 。
③ 通过语法分析得到一个查询树。
④ 通过索引存储将索引读入到内存。
⑤ 利用查询树搜索索引,从而得到每个词(Term) 的文档链表,对文档链表进行交、差、并得到结果文档。
⑥ 将搜索到的结果文档对查询的相关性进行排序。
⑦ 返回查询结果给用户。

文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-786235.html
ES写数据分别是写入一个新的文档和在原有文档的基础上进行数据的追加(覆盖原有的文档)。两者基本上没有什么区别,后者是把原来的文档进行删除,再重新写入。
ES写数据流程:
(1) 客户端选择一个ES节点发送写请求,ES节点接收请求变为协调节点。
(2) 协调节点判断写请求中如果没有指定文档id,则自动生成一个doc_id。协调节点对doc_id进行哈希取值,判断出文档应存储在哪个切片中。协调节点找到存储切片的对应节点位置,将请求转发给对应的node节点。
(3) Node节点的primary shard处理请求,并将数据同步到replica shard
(4) 协调节点发现所有的primary shard和所有的replica shard都处理完之后,就返回结果给客户端。
五. ES存储和查询数据
1.存储megacorp公司员工的信息,包含员工first_name,last_name,age,interests
#存储员工信息
PUT /megacorp/employee/1
{
"frist_name":"sam",
"last_name":"tom",
"interests":["swmming","basketball","music"],
"about":"I love coding",
"age":25
}
PUT /megacorp/employee/2
{
"frist_name":"Smith",
"last_name":"Math",
"interests":["basketball","music"],
"about":"I love coding",
"age":32
}
PUT /megacorp/employee/3
{
"frist_name":"Jone",
"last_name":"KeByt",
"interests":["music"],
"about":"I love coding",
"age":40
}megacorp为索引,代表公司(数据库),employee代表类型,表示员工表,数字1,2,3代表员工1,2,3
分词存储员工信息,使用mapping映射存储结构,同时设置字段的分词细粒度
分词:例如:司马玉龙,可以分解为司马,玉龙,司,马,玉,龙。查询的时候如果条件在分词里面,可以查询到该文档,比如电商平台的搜索依靠的也是分词搜索商品,直接将类似(包含关键字)的商品带出。
#ik_max_word 代表最大分词细粒度分解字段
POST /employees/slae/
{
"mappings":{
"perperties":{
"frist_name":{
"type": "text"
},
"last_name":{
"type": "text"
},
"full_name":{
"type": "text",
"analyzer":"ik_max_word",
"search_analyzer":"ik_max_word"
},
"address":{
"type":"text",
"analyzer":"ik_max_word",
"search_analyzer":"ik_max_word"
},
"sex":{
"type":"text"
},
"salay":{
"type":"text"
}
}
}
}2.查询员工信息
(1)查询所有员工信息
GET /megacorp/employee/_search结果,将搜索的结果集存放在hits里面

(2)条件查询
依靠员工last_name查询
#条件查询
GET /megacorp/employee/_search?q=last_name:tom文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-786235.html

依靠员工frist_name查询
GET /megacorp/employee/_search
{
"query":{
"match": {
"frist_name": "sam"
}
}
}过滤查询,先执行filter的条件,在执行query里面的条件
filter过滤可以有 range(范围),exists(存在),ids(文档id),term,terms(字段) 过滤,下面举例range,其他条件类似。
#filter过滤,相当于mysql 大于小于范围查询
GET /megacorp/employee/_search
{
"query":{
"bool":{
"must": {
"match":
{
"frist_name":"sam"
}
},
"filter": [
{
"range": {
"age": {
"gte": 20,
"lte": 40
}
}
}
]
}
}
}term(分析)搜索
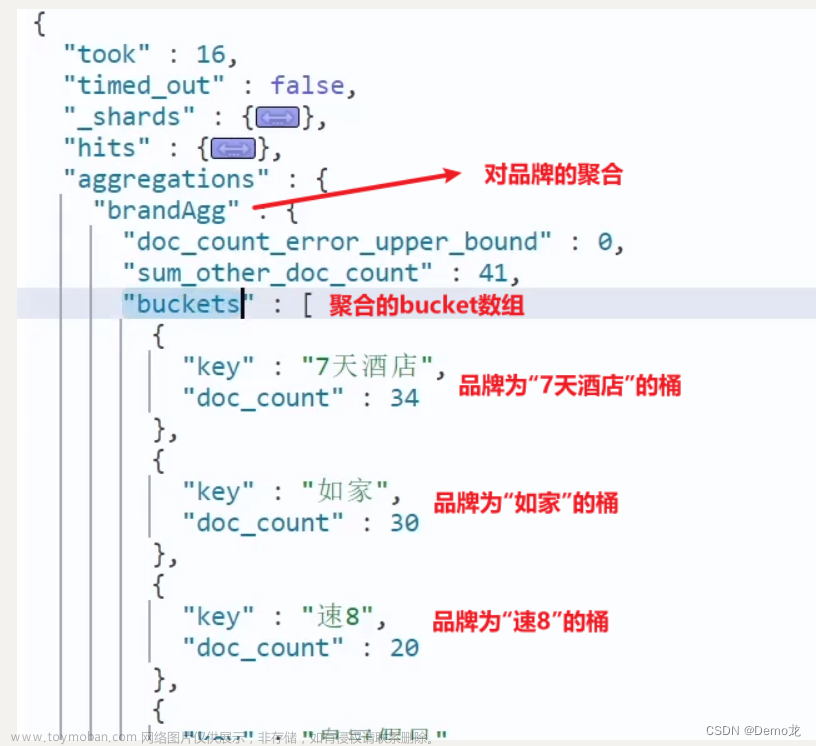
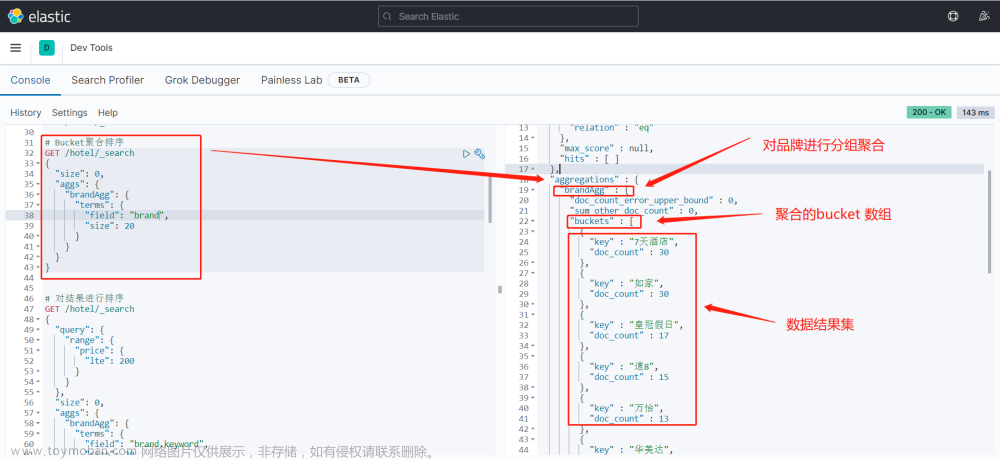
类似于myql的group by 分组查询
前提是查询的字段具有分词结构,即设置了analyzer
GET /megacorp/employee/_search
{
"aggs":{
"all_address":{
"terms":{
"field":"address"
}
}
}
}
在没有分词结构的基础上查询出现,文本字段不是分析排序结构,所有操作不能依靠默认进行。
GET /megacorp/employee/_search
{
"aggs":{
"all_address":{
"terms":{
"field":"frist_name"
}
}
}
}
短语搜索
GET /megacorp/employee/_search
{
"query":{
"match_phrase": {
"frist_name": "smith"
}
}
}高亮搜索
GET /megacorp/employee/_search
{
"query":{
"match_phrase": {
"frist_name": "smith"
}
},
"highlight":{
"fields": {
"frist_name": {}
}
}
}

(3)深入-高级搜索
结构搜索
精确搜索
使用_bulk 一次性插入多条数据
POST /my_store/products/_bulk
{ "index": { "_id": 1 }}
{ "price" : 10, "productID" : "XHDK-A-1293-#fJ3" }
{ "index": { "_id": 2 }}
{ "price" : 20, "productID" : "KDKE-B-9947-#kL5" }
{ "index": { "_id": 3 }}
{ "price" : 30, "productID" : "JODL-X-1937-#pV7" }
{ "index": { "_id": 4 }}
{ "price" : 30, "productID" : "QQPX-R-3956-#aD8" }term精确搜索
GET /my_store/products/_search
{
"query" : {
"constant_score" : {
"filter" : {
"term" : {
"price" : 20
}
}
}
}
}term为简单的精准查询,就像mysql中的sql
select * from products where price = 20constant_score的意思是不评分计算查询,将term转换成filter过滤。
组合过滤器-bool过滤器
结构
GET /my_store/products/_search
{
"query":{
"bool": {
"should": [
{}
],
"must": [
{}
],
"must_not": [
{}
]
}
}
}should:与myql的OR等价。
must:与mysql的AND等价。
must_not:与mysql的NOT等价。
例:查询价格在10~20的文档
mysql:select * from products where price >= 10 and pirce<=20
GET /my_store/products/_search
{
"query":{
"bool": {
"should": [
{
"constant_score": {
"filter": {
"range": {
"price": {
"gte": 10,
"lte": 20
}
}
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
嵌套bool
查询sql
SELECT document
FROM products
WHERE productID = "KDKE-B-9947-#kL5"
OR ( productID = "JODL-X-1937-#pV7"
AND price = 30 )转成DSL
{
"query":{
"constant_score": {
"filter": {
"bool": {
"should":[
{
"term":{
"productID":"KDKE-B-9947-#kL5"
}
},
{
"bool":{
"must":[
{
"term":
{
"productID":"JODL-X-1937-#pV7"
}
},
{
"term":
{
"price":30
}
}
]
}
}
]
}
},
"boost": 1.2
}
}
}多个精确搜索
使用terms多条件精准查询
GET /my_store/products/_search
{
"query":{
"constant_score": {
"filter": {
"terms": {
"price": [20,30]
}
},
"boost": 1.2
}
}
}处理空值NULL
POST /my_index/posts/_bulk
{ "index": { "_id": "1" }}
{ "tags" : ["search"] }
{ "index": { "_id": "2" }}
{ "tags" : ["search", "open_source"] }
{ "index": { "_id": "3" }}
{ "other_field" : "some data" }
{ "index": { "_id": "4" }}
{ "tags" : null }
{ "index": { "_id": "5" }}
{ "tags" : ["search", null] } mysql语句
SELECT tags
FROM posts
WHERE tags IS NOT NULLES-DSL,使用exists判断
GET /my_index/posts/_search
{
"query" : {
"constant_score" : {
"filter" : {
"exists" : { "field" : "tags" }
}
}
}
}match搜索
match搜索本质是多个term搜索的结果集,多个term搜索之后合并,如果有分词,则返回有分词的结果,没有分词就返回直接查询,match是匹配查询,即全文中有没有匹配这个单词的,有匹配的带出。
GET /employees/slae/_search
{
"query":{
"match": {
"full_name": "lisisi"
}
}
}POST /my_index/my_type/_bulk
{ "index": { "_id": 1 }}
{ "title": "The quick brown fox" }
{ "index": { "_id": 2 }}
{ "title": "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog" }
{ "index": { "_id": 3 }}
{ "title": "The quick brown fox jumps over the quick dog" }
{ "index": { "_id": 4 }}
{ "title": "Brown fox brown dog" }单个单词匹配
GET /my_index/my_type/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"title": "QUICK!"
}
}
}组合查询
GET /my_index/my_type/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": { "match": { "title": "quick" }},
"must_not": { "match": { "title": "lazy" }},
"should": [
{ "match": { "title": "brown" }},
{ "match": { "title": "dog" }}
]
}
}
}3.删除员工信息
#删除员工1
DELETE /megacorp/employee/14.修改员工信息
#修改员工1的信息
PUT /megacorp/employee/1
{
"frist_name":"smith",
"last_name":"ttm",
"interests":["swmming","basketball","music"],
"about":"I love coding",
"age":25
}
语法介绍到这里,篇幅太长,可以参考https://www.elastic.co/guide/cn/elasticsearch/guide/
六. ES整合Springboot
1.引入依赖
Springboot版本2.5,引入2.7es
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.jcraft</groupId>
<artifactId>jsch</artifactId>
<version>0.1.55</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework.boot/spring-boot-starter-web -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.elasticsearch.client/elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId>
<!-- <version>7.15.0</version>-->
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch</artifactId>
<!-- <version>3.0.2</version>-->
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--rabbitmq-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.netty</groupId>
<artifactId>netty-all</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-websocket</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>2.创建RestHightClient配置
@Configuration
public class RestHighClient extends AbstractElasticsearchConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@Override
public RestHighLevelClient elasticsearchClient() {
final ClientConfiguration clientConfiguration = ClientConfiguration
.builder()
.connectedTo("192.168.219.137:9200")
.build();
return RestClients.create(clientConfiguration).rest();
}
}3.创建实体类
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Document(indexName = "teacher",createIndex = true)
public class Teacher {
@Id
@Field(store = true,type = FieldType.Keyword)
private String id;
@Field(store = true,type = FieldType.Text)
private String teacherName;
@Field(store = true,type = FieldType.Text)
private String email;
@Field(store = true,type = FieldType.Text,analyzer = "ik_max_word")
private String address;
@Field(store = true,type = FieldType.Text)
private String phone;
}@Document表示创建实体类的同时创建ES文档,并将实体类的字段都当成是ES中的字段,
@Field中可以规定字段的类型和是否进行分词
4.创建ES映射仓库
@Component
public interface EsTeacherMapper extends ElasticsearchRepository<Teacher,String> {
}接口继承ElasticsearchReposity接口,接口里面集成了增删改查的方法,这里的用法很便捷,非常类似MybatisPlus的用法,用过MybatisPlus的小伙伴应该很容易上手。
5.调用接口实现操作
@SpringBootTest
class ElasticsearchApplicationTests {
@Resource
RestHighClient restHightClient;
@Autowired
EsTeacherMapper teacherMapper;
@Test
public void PutData(){
Teacher teacher = new Teacher();
teacher.setId("A00003");
teacher.setTeacherName("陈平安");
teacher.setPhone("34546565265");
teacher.setEmail("2435454656@qq.com");
teacher.setAddress("大丽龙泉县落魄山竹楼");
Teacher save = teacherMapper.save(teacher);
System.out.println(save);
}
@Test
public void query() throws IOException {
/**
* 依靠id查询
*/
Optional<Teacher> a00001 = teacherMapper.findById("A00002");
System.out.println(a00001.get());
/**
* 查询所有
*/
Iterable<Teacher> all = teacherMapper.findAll();
all.forEach(teacher -> System.out.println(teacher));
/**
* 条件查询
*/
MultiMatchQueryBuilder multiMatchQueryBuilder = QueryBuilders
.multiMatchQuery("竹楼", "address");
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("teacher");
SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
searchSourceBuilder.query(multiMatchQueryBuilder);
searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);
SearchResponse search = restHightClient.elasticsearchClient().search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
SearchHit[] hits = search.getHits().getHits();
for (SearchHit hit: hits) {
System.out.println(hit.getIndex()+":"+hit.getSourceAsString());
}
}
/**
*filter查询
**/
@Test
public void filterQuery() throws IOException {
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("teacher");
SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
searchSourceBuilder
.query(QueryBuilders.termQuery("address","解放"))
.postFilter(QueryBuilders.idsQuery().addIds("A00001"));
searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);
SearchResponse search = restHightClient.elasticsearchClient()
.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
SearchHit[] hits = search.getHits().getHits();
for (SearchHit showHit:hits) {
System.out.println(showHit.getSourceAsString());
}
searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("address","解放"));
searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);
SearchResponse response = restHightClient.elasticsearchClient()
.search(searchRequest,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
SearchHit[] hits1 = response.getHits().getHits();
for (SearchHit searchHit: hits1) {
System.out.println(searchHit.getSourceAsString());
}
}
}存放数据

查询数据
依靠id查询
 查询所有数据
查询所有数据

match条件查询
 filter过滤查询
filter过滤查询

结语
代码虐我千百遍,待它如初恋,卖油翁小故事,无他,唯手熟尔。
到了这里,关于ES数据存储搜索引擎入门到整合Springboot一章直达的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!