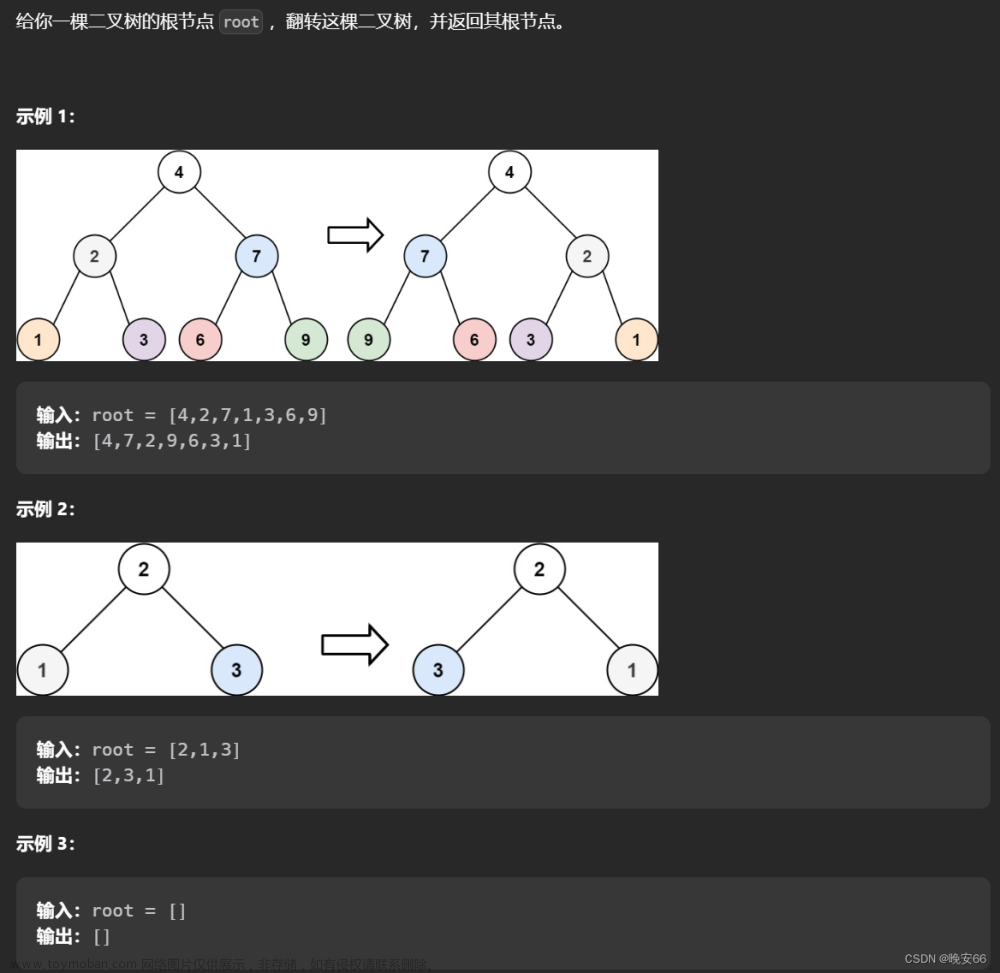
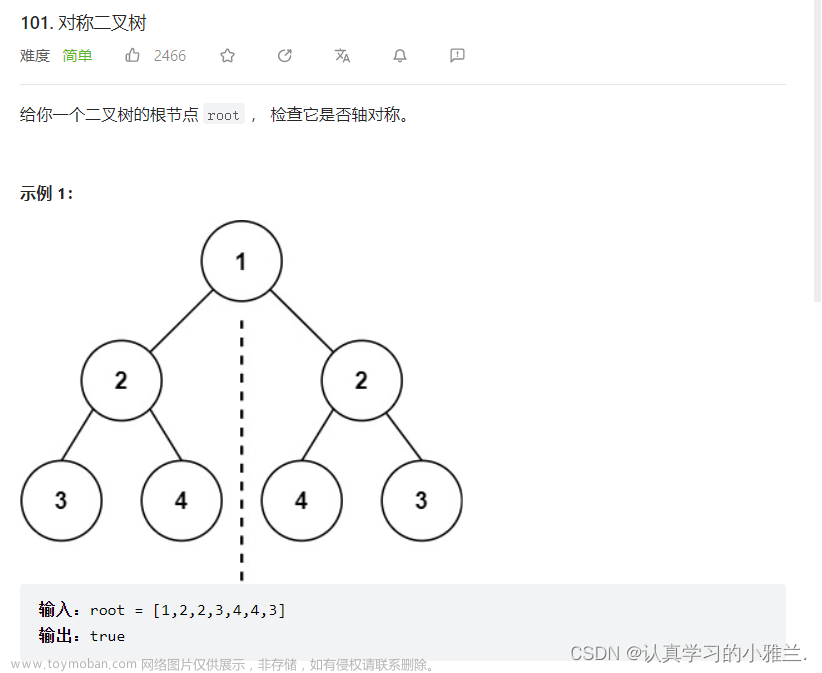
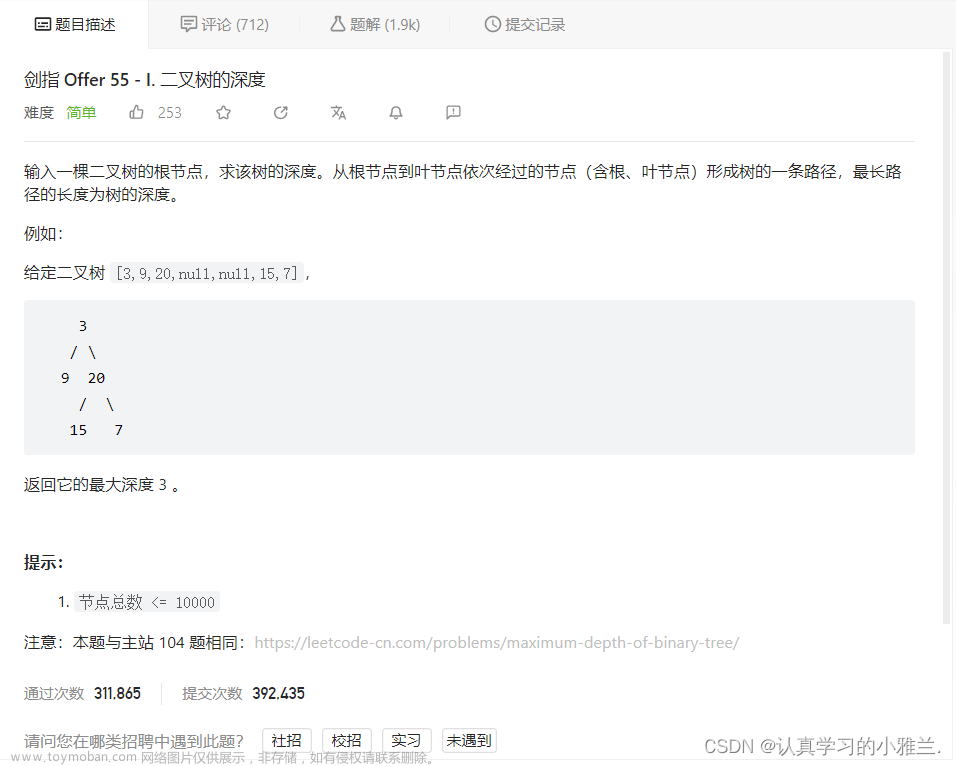
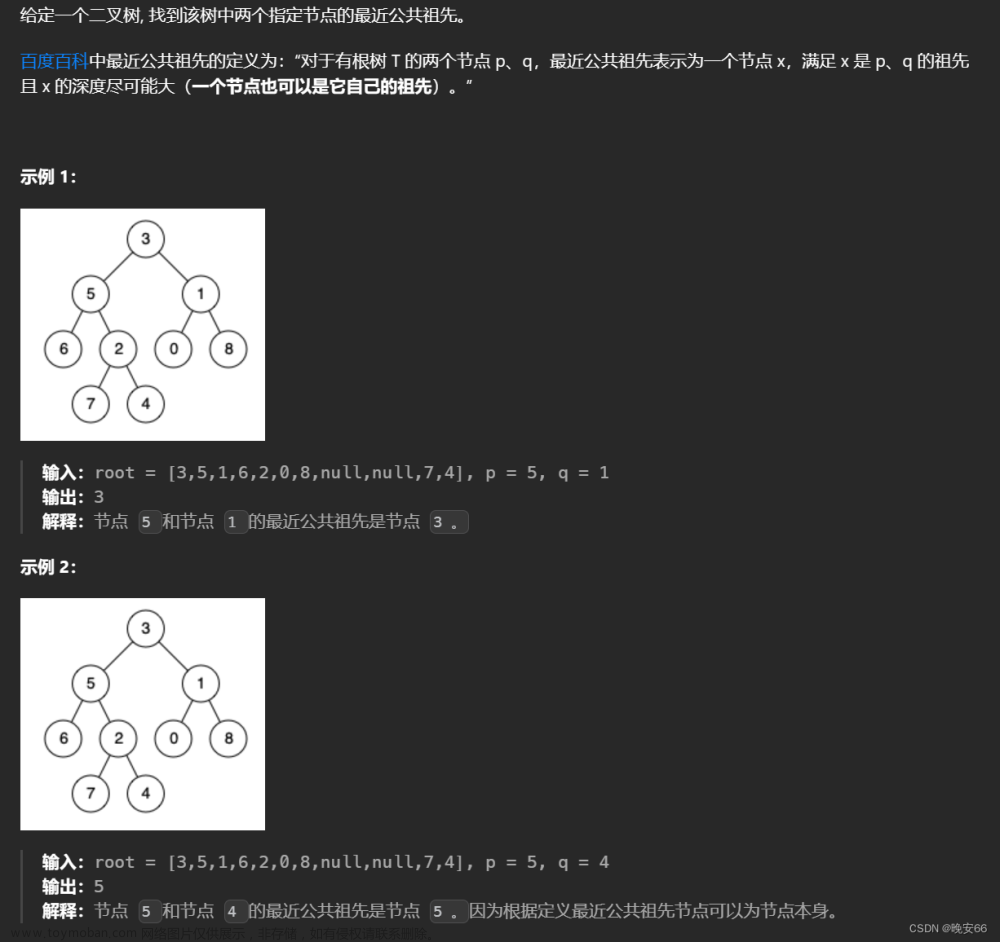
二叉树的定义
二叉树(Binary Tree)是一种常见的树形结构,它由节点(Node)和节点之间的关系构成。每个节点最多有两个子节点,分别称为左子节点和右子节点。二叉树中的每个节点可以为空(null)。

二叉树的性质
- 每个节点最多有两个子节点:每个节点最多有一个左子节点和一个右子节点。这意味着一个节点的度数(Degree)最大为2。
- 左子树和右子树的顺序是固定的:在二叉树中,左子树位于父节点的左侧,右子树位于父节点的右侧。改变左右子树的顺序将产生不同的二叉树。
- 节点的度数:节点的度数是指该节点的子节点数量。二叉树中,节点的度数最大为2,即一个节点最多有两个子节点。
- 叶节点(叶子节点):叶节点是没有子节点的节点,也可以称为终端节点。
- 节点的层级(Level):根节点的层级为1,其余节点的层级为其父节点的层级加1。
- 树的高度(Height):树的高度是从根节点到最远叶节点的最长路径上的边数。叶节点的高度为0,空树的高度为-1。
- 完全二叉树(Complete Binary Tree)性质:在完全二叉树中,除了最后一层外,其他层的节点都是满的,且最后一层的节点都尽量靠左排列。
- 满二叉树(Full Binary Tree)性质:在满二叉树中,除了叶节点外,每个节点都有两个子节点。
- 二叉搜索树(Binary Search Tree)性质:二叉搜索树是一种特殊的二叉树,它满足以下性质:对于树中的每个节点,其左子树中的所有节点都小于该节点的值,而其右子树中的所有节点都大于该节点的值。
- 若规定根结点的层数为1,则一棵非空二叉树的第i层上最多有 2^(i-1) (i > 0)个结点。
- 若规定只有根结点的二叉树的深度为1,则深度为K的二叉树的最大结点数是 2^k - 1 (k>=0)。
- 对任何一棵二叉树, 如果其叶结点个数为 n0,度为2的非叶结点个数为 n2,则有 n0 = n2 + 1。
- 具有n个结点的完全二叉树的深度k为log2 (n + 1) 上取整。
- 对于具有n个结点的完全二叉树,如果按照从上至下从左至右的顺序对所有节点从0开始编号,则对于序号为 i 的结点有:
若 i > 0,双亲序号:(i - 1) / 2;i = 0,i 为根结点编号,无双亲结点。
若 2i + 1< n,左孩子序号:2i + 1,否则无左孩子。
若 2i + 2 < n,右孩子序号:2i + 2,否则无右孩子。
二叉树的存储
二叉树可以使用不同的数据结构进行存储。以下是几种常见的二叉树存储方式:
- 链式存储(Linked Storage):使用节点对象和指针来表示二叉树的结构。每个节点对象包含存储的数据以及指向左子节点和右子节点的指针。这种存储方式可以直观地表示树的结构,适用于任意形状的二叉树。Java中常用的LinkedList数据结构可以用来实现二叉树的链式存储。
- 数组存储(Array Storage):使用数组来表示二叉树的结构。可以使用一维数组或二维数组来存储节点的数据。通过数组的索引关系来表示节点之间的父子关系。这种存储方式可以节省存储空间,但适用于完全二叉树或满二叉树等具有规律结构的二叉树。
- 堆存储(Heap Storage):使用堆(Heap)数据结构来存储二叉树。堆是一种特殊的完全二叉树,通常使用数组来实现。在堆存储中,节点的位置是通过数组的索引来确定的。堆存储常用于实现优先队列等应用。
二叉树的实现
class TreeNode {
public char val;
public TreeNode left; // 左孩子引用
public TreeNode right; // 右孩子引用
public TreeNode(char val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
A
/ \
B C
/ \ \
D E F
TreeNode root = new TreeNode('A');
root.left = new TreeNode('B');
root.right = new TreeNode('C');
root.left.left = new TreeNode('D');
root.left.right = new TreeNode('E');
root.right.right = new TreeNode('F');
二叉树的遍历方法
- 前序遍历(Preorder Traversal):先访问根节点,然后按照左子树、右子树的顺序递归遍历子树。
- 遍历结果:A -> B -> D -> E -> C -> F
- 中序遍历(Inorder Traversal):先按照左子树、根节点、右子树的顺序递归遍历子树。
- 遍历结果:D -> B -> E -> A -> C -> F
- 后序遍历(Postorder Traversal):先按照左子树、右子树的顺序递归遍历子树,最后访问根节点。
- 遍历结果:D -> E -> B -> F -> C -> A
- 层序遍历(Level Order Traversal):从上到下逐层遍历二叉树的节点。
- 遍历结果:A -> B -> C -> D -> E -> F
-
s形层次遍历
-
遍历结果:A -> C -> B -> D -> E -> F
-
递归实现
public void preOrder(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return;
System.out.print(root.val+" ");
preOrder(root.left);
preOrder(root.right);
}
public void inOrder(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return;
inOrder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.val+" ");
inOrder(root.right);
}
public void postOrder(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return;
postOrder(root.left);
postOrder(root.right);
System.out.print(root.val+" ");
}非递归实现
public void preOrderIteration(TreeNode head) {
if(head==null) {
return;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<>();
stack.push(head);
while(!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNOde node=stack.pop();
System.out.print(node.val+" ");
if(node.right!=null) {
stack.push(node.left);
}
if(node.left!=null) {
stack.push(node.right);
}
}
}
public void inOrderIteration(TreeNode head) {
if(head==null) {
return;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur=head;
while(!stack.isEmpty()) {
while(cur!=null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur=cur.left;
}
TreeNode node=stack.pop();
System.out.print(node.val+"");
if(node.right!=null) {
cur=node.right;
}
}
}
public static void postOrderIteration(TreeNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack1 = new Stack<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack2 = new Stack<>();
stack1.push(head);
while (!stack1.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = stack1.pop();
stack2.push(node);
if (node.left != null) {
stack1.push(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
stack1.push(node.right);
}
}
while (!stack2.isEmpty()) {
System.out.print(stack2.pop().val + " ");
}
}层次遍历
/**
* 二叉树的层次遍历
*/
public void levelOrder() {
BtNode ptr = root;
Queue<BtNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(ptr);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
ptr = queue.poll();
System.out.print(ptr.getDate() + " ");
if (ptr.getLeftChild() != null) {
queue.offer(ptr.getLeftChild());
}
if (ptr.getRightChild() != null) {
queue.offer(ptr.getRightChild());
}
}
}
s形层次遍历
/**
* 二叉树的s遍历
*/
public void sOrder() {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
BtNode ptr = root;
Stack<BtNode> stack1 = new Stack<>();
Stack<BtNode> stack2 = new Stack<>();
stack1.push(ptr);
while (!stack1.isEmpty() || !stack1.isEmpty()) {
while (!stack1.isEmpty()) {
ptr = stack1.pop();
System.out.print(ptr.getDate() + " ");
if (ptr.getLeftChild() != null) {
stack2.push(ptr.getLeftChild());
}
if (ptr.getRightChild() != null) {
stack2.push(ptr.getRightChild());
}
}
while (!stack2.isEmpty()) {
ptr = stack2.pop();
System.out.print(ptr.getDate() + " ");
if (ptr.getRightChild() != null) {
stack1.push(ptr.getRightChild());
}
if (ptr.getLeftChild() != null) {
stack1.push(ptr.getLeftChild());
}
}
}
}
计算二叉树的节点个数
/**
* 获取二叉树的结点个数
*/
private int getSize(BtNode ptr) {
if (ptr == null) {
return 0;
}
return getSize(ptr.getLeftChild()) + getSize(ptr.getRightChild()) + 1;
}
public int getSize() {
return getSize(root);
}
计算二叉树的高度(深度)
/**
* 计算二叉树的高度
*/
private int getDepth(BtNode ptr) {
if (ptr == null) {
return 0;
}
return Math.max(getDepth(ptr.getLeftChild()), getDepth(ptr.getRightChild())) + 1;
}
判断二叉树是否是一颗满二叉树
/**
* 判断是否是一颗满二叉树
*/
public boolean isFullBinaryTree() {
BtNode ptr = root;
boolean tag = true;
Deque<BtNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
int n = 1;
queue.offer(ptr);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int i = 0;
for (; i < n; ++i) {
ptr = queue.poll();
if (ptr == null) {
break;
}
if (ptr.getLeftChild() != null) {
queue.offer(ptr.getLeftChild());
}
if (ptr.getRightChild() != null) {
queue.offer(ptr.getRightChild());
}
}
if (i != n) {
tag = false;
break;
}
n *= 2;
}
return tag;
}
判断二叉树是否是一颗完全二叉树
/**
* 判断是否是一个完全二叉树
*/
public boolean isComBinaryTree() {
BtNode ptr = root;
boolean tag = true;
Deque<BtNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(ptr);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
ptr = queue.poll();
if (ptr == null) {
break;
}
queue.offer(ptr.getLeftChild());
queue.offer(ptr.getRightChild());
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
BtNode poll = queue.poll();
if (poll != null) {
tag = false;
break;
}
}
return tag;
}
利用前序遍历和中序遍历构建二叉树
 文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-829729.html
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-829729.html
/**
* 根据前序遍历和中序遍历构建二叉树
*/
private BtNode createTreeByPreIn(String pre, String in, int len) {
BtNode s = null;
if (len > 0) {
s = new BtNode(pre.charAt(0));
//通过前序遍历在中序遍历中找到根节点的下标(下标为0的位置)
int pos = in.indexOf(pre.charAt(0));
//没有找到则异常退出
if (-1 == pos) {
System.exit(-1);
}
s.setLeftChild(createTreeByPreIn(pre.substring(1, pos + 1), in.substring(0, pos), pos));
s.setRightChild(createTreeByPreIn(pre.substring(pos + 1, len), in.substring(pos + 1, len), len - pos - 1));
}
return s;
}
public void createTreeByPreIn(String pre, String in) {
if (pre == null || in == null) {
root = null;
}
root = createTreeByPreIn(pre, in, pre.length());
}
利用后序遍历和中序遍历构建二叉树
 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-829729.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-829729.html
/**
* 根据后序遍历和中序遍历构建二叉树
*/
private BtNode createTreeByPostIn(String post, String in, int len) {
BtNode s = null;
if (len > 0) {
s = new BtNode(post.charAt(len - 1));
//通过后序遍历在中序遍历中找到根节点的下标(下标为len - 1的位置)
int pos = in.indexOf(post.charAt(len - 1));
//没有找到则异常退出
if (-1 == pos) {
System.exit(-1);
}
s.setLeftChild(createTreeByPostIn(post.substring(0, pos), in.substring(0, pos), pos));
s.setRightChild(createTreeByPostIn(post.substring(pos,len - 1),in.substring(pos + 1,len),len - pos - 1));
}
return s;
}
public void createTreeByPostIn(String post, String in) {
if (post == null || in == null) {
root = null;
}
root = createTreeByPostIn(post, in, post.length());
}
到了这里,关于leetcode-二叉树的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!