源码来自[https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34467412/article/details/90738232],作者也是对论文作者ResNet框架的复现,而我是在chatGPT帮助下把博主TensorFlow的代码改成了pytorch代码。
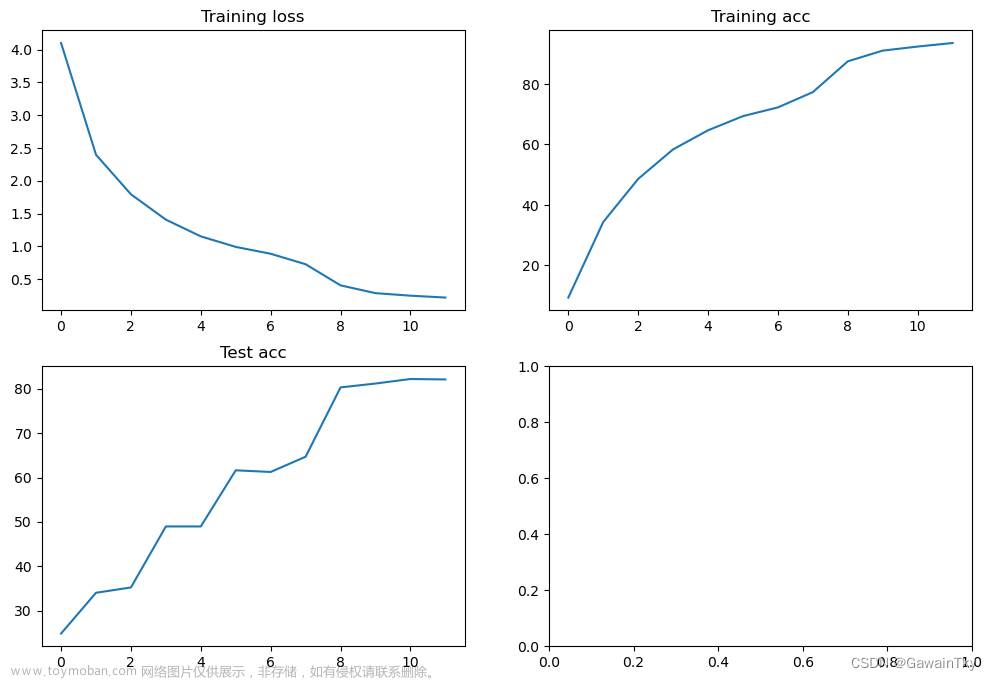
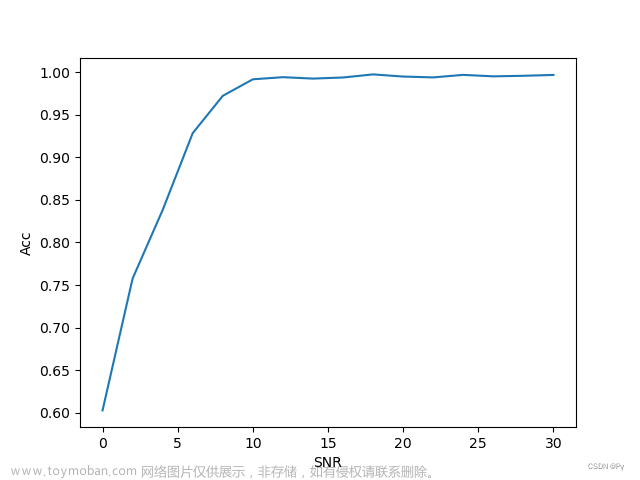
由于硬件限制,并没有使用完整的数据集,仅对前10种调制模型进行识别,全信噪比情况下测试集识别率可达72%;仅考虑0:30dB情况下测试集识别率可达94%。
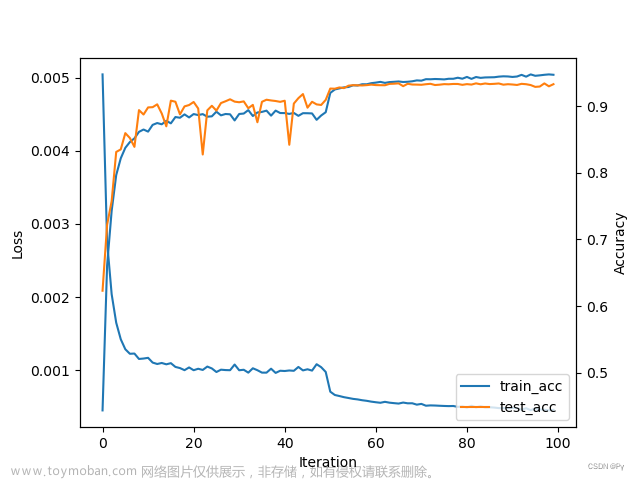
训练过程
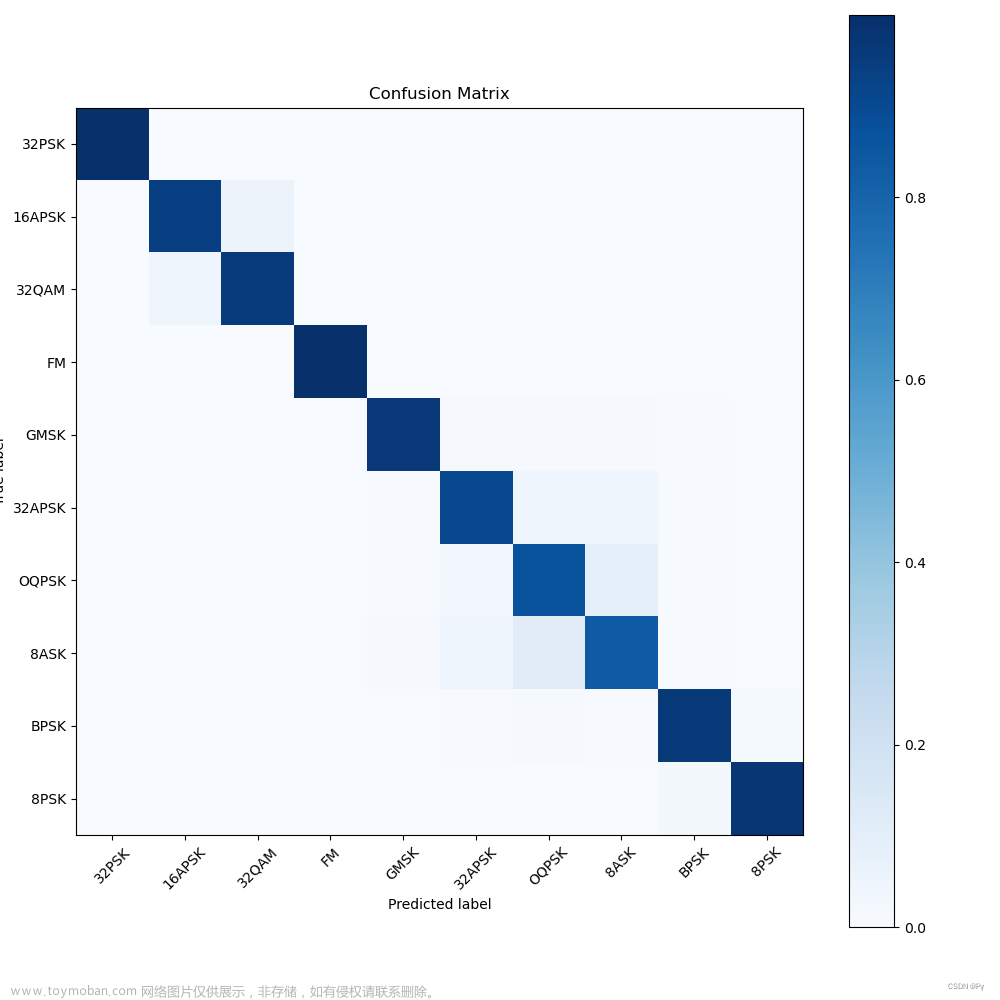
测试集上的混淆矩阵
不同信噪比下的识别率
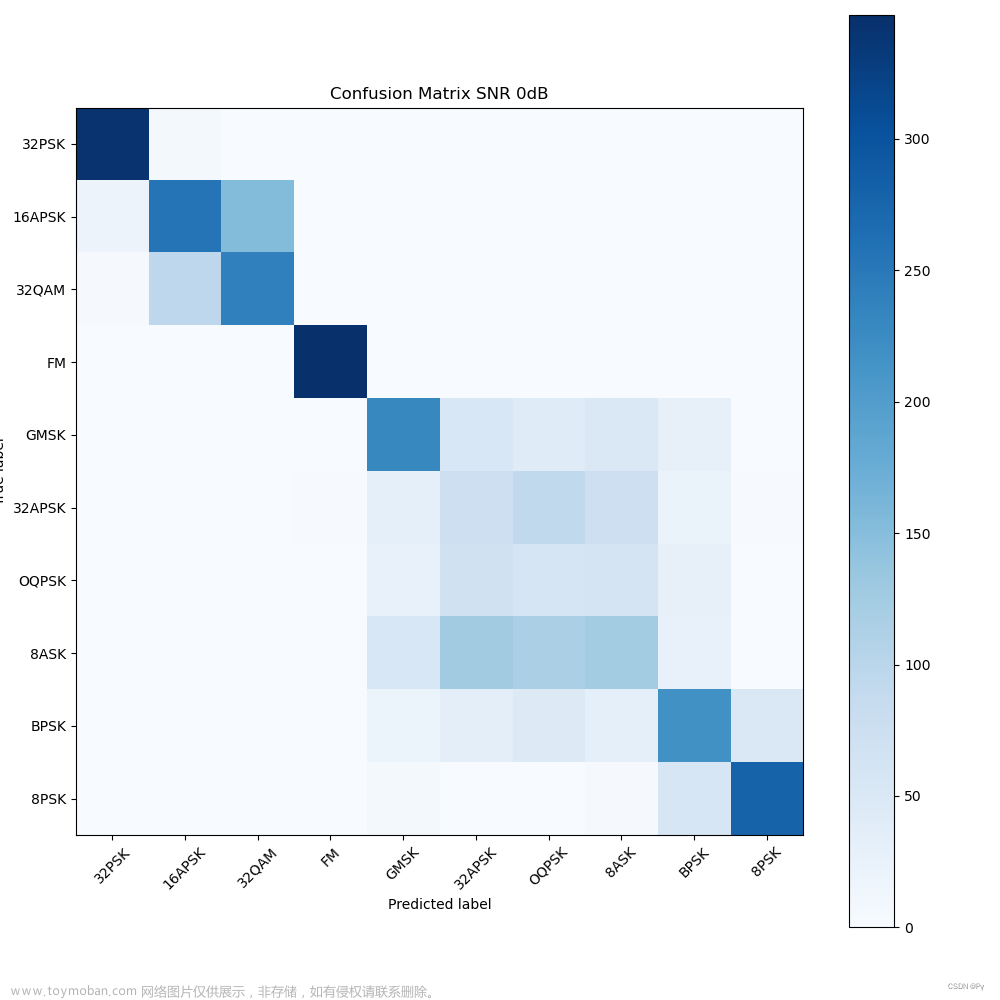
信噪比为0db时候的混淆矩阵文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-536586.html
 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-536586.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-536586.html
网络部分
class ResidualStack(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_channels, output_channels, kernel_size, seq, pool_size):
super(ResidualStack, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(input_channels, output_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding='same') # (kernel_size-1)//2保证输入输出形状一样
# Residual Unit 1
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(output_channels, 32, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=1, padding='same')
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(32, output_channels, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=1, padding='same')
# Residual Unit 2
self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(output_channels, 32, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=1, padding='same')
self.conv5 = nn.Conv2d(32, output_channels, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=1, padding='same')
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=pool_size, stride=pool_size)
self.seq = seq
def forward(self, x):
# Residual Unit 1
x = self.conv1(x)
shortcut = x
x = self.conv2(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = self.conv3(x)
x = x + shortcut
x = F.relu(x)
# Residual Unit 2
shortcut = x
x = self.conv4(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = self.conv5(x)
x = x + shortcut
x = F.relu(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
return x
class MyResNet(nn.Module): # 1,1024,2
def __init__(self, num_classes):
super(MyResNet, self).__init__()
self.num_classes = num_classes
# self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(1)
self.seq1 = ResidualStack(1, 32, kernel_size=(3, 2), seq="ReStk0", pool_size=(2, 2))
self.seq2 = ResidualStack(32, 32, kernel_size=(3, 1), seq="ReStk1", pool_size=(2, 1))
self.seq3 = ResidualStack(32, 32, kernel_size=(3, 1), seq="ReStk2", pool_size=(2, 1))
self.seq4 = ResidualStack(32, 32, kernel_size=(3, 1), seq="ReStk3", pool_size=(2, 1))
self.seq5 = ResidualStack(32, 32, kernel_size=(3, 1), seq="ReStk4", pool_size=(2, 1))
self.seq6 = ResidualStack(32, 32, kernel_size=(3, 1), seq="ReStk5", pool_size=(2, 1))
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(512, 128) # 64 rml, 192 mnist, 512 rml2018
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(128, num_classes)
self.dropout = nn.AlphaDropout(0.2)
def forward(self, x):
# x = self.bn(x)
x = self.seq1(x)
x = self.seq2(x)
x = self.seq3(x)
x = self.seq4(x)
x = self.seq5(x)
x = self.seq6(x)
x = torch.flatten(x,start_dim=1)
x = self.fc1(x)
x = F.selu(x)
x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
return x混淆矩阵代码
def plot_confusion_matrix(dataloader, model, classes):
# pre-progression
num_classes = len(classes)
matrix = torch.zeros(size=(num_classes,num_classes))
for x, y in dataloader:
y_pred = model(x)
for i in range(y.size(0)):
matrix[y_pred[i].argmax()][y[i].argmax()] += 1
for i in range(0, num_classes):
matrix[i, :] = matrix[i, :] / torch.sum(matrix[i, :])
# configuration of plot
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.imshow(matrix, interpolation='nearest', cmap=plt.cm.Blues)
# interpolation插值影响图像显示效果
tick_marks = np.arange(num_classes)
plt.xticks(tick_marks, classes, rotation=45)
plt.yticks(tick_marks, classes)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.title('Confusion Matrix')
plt.colorbar()
plt.xlabel('Predicted label')
plt.ylabel('True label')
plt.show()
return matrix信噪比准确率,信噪比混淆矩阵代码
def plot_snr_curves(x, y, snr, model, classes):
if not x[0].is_cuda:
model.cpu()
num_classes = len(classes)
snr = snr.reshape((len(snr)))
snrs, counts = np.unique(snr, return_counts=True)
num_snrs = len(snrs)
acc = np.zeros(num_snrs)
matrix = torch.zeros(size=(num_snrs, num_classes, num_classes))
for i in range(num_snrs):
x_snr = x[snr==snrs[i]]
y_snr = y[snr==snrs[i]]
temp_dataset = Data.TensorDataset(x_snr, y_snr)
temp_dataloader = DataLoader(dataset=temp_dataset, batch_size=256)
for temp_x, temp_y in temp_dataloader:
y_pred = model(temp_x)
acc[i] += (y_pred.argmax(1) == temp_y.argmax(1)).sum()
for k in range(temp_y.size(0)):
matrix[i][y_pred[k].argmax()][temp_y[k].argmax()] += 1
acc = acc / counts
plt.plot(snrs, acc)
plt.xlabel('SNR')
plt.ylabel('Acc')
plt.show()
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.imshow(matrix[0][:][:], interpolation='nearest', cmap=plt.cm.Blues)
# interpolation插值影响图像显示效果
tick_marks = np.arange(num_classes)
plt.xticks(tick_marks, classes, rotation=45)
plt.yticks(tick_marks, classes)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.title('Confusion Matrix SNR 0dB')
plt.colorbar()
plt.xlabel('Predicted label')
plt.ylabel('True label')
plt.show()
return matrix重新配置信号的label
def select(y, classes, classes_included=True):
temp = y.sum(axis=0)
one_zero = (temp >= 1) # 哪些地方是label的
index = [i for i, x in enumerate(one_zero) if x] # 得到label的位置
new_classes = []
new_num_classes = one_zero.sum()
for i in range(new_num_classes):
new_classes.append(classes[index[i]])
new_y = np.zeros((y.shape[0], new_num_classes))
y_index = y.argmax(1) # y=1的位置
for i in range(y_index.shape[0]):
new_y[i][y_index[i]] = 1
if classes_included:
return new_y, new_classes
else:
return new_y训练和测试代码
def train(model, train_dataloader, itr, optimizer, loss_func):
start_time = time.time()
train_loss = 0
train_accuracy = 0
model.train()
for x, y in train_dataloader:
optimizer.zero_grad() # 梯度清零
y_pred = model(x) # 计算预测标签
loss = loss_func(y_pred, y.argmax(dim=1)) # 计算损失, argmax() for one-hot
loss.backward() # 利用反向传播计算gradients
optimizer.step() # 利用gradients更新参数值
train_accuracy += (y_pred.argmax(1) == y.argmax(1)).sum()
train_loss += loss.item()
ep_loss = train_loss / len(train_dataloader.dataset)
ep_train_acc = train_accuracy / len(train_dataloader.dataset)
end_time = time.time()
print("Epoch:", itr + 1,
"\nTraining Loss: ", round(ep_loss,5),
"Training Accuracy: ", round(ep_train_acc.item(), 5))
print("Training time consuming: {}".format(end_time-start_time))
return ep_loss, ep_train_acc
def test(model,test_dataloader):
# test
test_accuracy = 0
model.eval()
for x, y in test_dataloader:
y_pred = model(x)
test_accuracy += (y_pred.argmax(1) == y.argmax(1)).sum()
ep_test_acc = test_accuracy / len(test_dataloader.dataset)
print("Test Accuracy: ", round(ep_test_acc.item(),5))
return ep_test_acc主程序
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Running Time
time = datetime.datetime.now()
month = time.month
day = time.day
# Configuration
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
# File path
path = 'data/SNR_greater_0_10data/'
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = np.load(path + 'X_train.npy'), np.load(path + 'X_test.npy'), np.load(path + 'Y_train.npy'), np.load(path + 'Y_test.npy')
y_train, classes = select(y_train, classes)
y_test = select(y_test, classes, False)
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = torch.from_numpy(x_train), torch.from_numpy(x_test), torch.from_numpy(y_train), torch.from_numpy(y_test)
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = x_train.to(device), x_test.to(device), y_train.to(device), y_test.to(device)
num_classes = len(classes)
train_mean, train_std = torch.mean(x_train), torch.std(x_train)
test_mean, test_std = torch.mean(x_test), torch.std(x_test)
train_transformer = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Normalize(mean=train_mean, std=train_std),
])
test_transformer = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Normalize(mean=test_mean, std=test_std),
])
x_train = train_transformer(x_train)
x_test = test_transformer(x_test)
x_train = resize(x_train, (x_train.shape[0], 1, 1024, 2))
x_test = resize(x_test, (x_test.shape[0], 1, 1024, 2))
print("Shape of x_train : {}".format(x_train.shape))
train_dataset = Data.TensorDataset(x_train, y_train)
train_dataloader = DataLoader(dataset=train_dataset,batch_size=256, shuffle=True)
test_dataset = Data.TensorDataset(x_test, y_test)
test_dataloader = DataLoader(dataset=test_dataset, batch_size=256, shuffle=True)
# Model
model = MyResNet(num_classes).to(device)
loss_function = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.005)
lr_scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer, step_size=50, gamma=0.1) # step decay
itrs = 100
train_loss = []
train_acc = []
test_acc = []
best_accuracy = 0
print("start training")
for itr in range(itrs):
epoch_loss, epoch_train_acc = train(model, train_dataloader, itr, optimizer, loss_function)
epoch_test_acc = test(model, test_dataloader)
train_loss.append(epoch_loss)
train_acc.append(epoch_train_acc)
test_acc.append(epoch_test_acc)
# Save best model on test data
if epoch_test_acc > best_accuracy:
best_accuracy = epoch_test_acc
torch.save(model, path + "ResNet_Identification_best_{}month_{}day.pth".format(month,day))
print("-----The best accuracy now is {}-----".format(best_accuracy))
print("-----The best model until now has been saved-----")
lr_scheduler.step()
confusion_matrix = plot_confusion_matrix(test_dataloader, model, classes)
# Accuracy and Loss
train_acc = [tensor.item() for tensor in train_acc]
test_acc = [tensor.item() for tensor in test_acc]
fig, ax1 = plt.subplots()
ax2 = ax1.twinx()
x = range(itrs)
ax1.plot(x, train_loss, label='train_loss')
ax2.plot(x, train_acc, label='train_acc')
ax2.plot(x, test_acc, label='test_acc')
ax1.set_xlabel('Iteration')
ax1.set_ylabel('Loss')
ax2.set_ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.show()到了这里,关于【写给自己】成功使用ResNet识别RML2018.a数据集的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!