opencv特征匹配方法有两种,分别是:
暴力特征匹配
BF(Brute-Force),暴力特征匹配方法。它使用第一组中的每个特征的描述子,与第二组中的所有特征描述子进行匹配,计算它们之间的差距,然后将最接近一个匹配返回。
FLANN特征匹配
在进行批量特征匹配时,FLANN速度更快。
由于它使用的是邻近近似值,所以精度较差。
Opencv特征匹配实现的简单过程:
第一步:定义特征检测器(SIFT,SURF,ORB等)。
第二步:对图像中特征点进行检测,并将特征点存储在Keypoints中。
第三步:提取特征点的描述信息。
第四步:定义特征匹配器(特征匹配的方法主要有两种分别为暴力匹配BFmatch和FlannBased)。
第五步:过滤掉较差的匹配点位(一般根据临近两点的距离进行过滤)
主要是根据DMatch中的distance进行过滤,对于distance可以抽象理解为匹配的分值,distance越小说明检测点的相似度越高,效果越好。
第六步:对匹配的特征点显示。
实现代码
代码1(未滤波,只限制筛选点数为20)
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include<opencv2\highgui\highgui.hpp>
#include<opencv2\imgproc\imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/xfeatures2d.hpp>
using namespace cv; //包含cv命名空间
using namespace std;
using namespace xfeatures2d;
int main() {
system("color 2E");
//载入图片
Mat src1 = imread("E:\\乔大花进度\\11-18\\sift特征检测和匹配\\3.jpg",1);
Mat src2 = imread("E:\\乔大花进度\\11-18\\sift特征检测和匹配\\4.jpg", 1);
//显示原图
imshow("原图1",src1);
imshow("原图2", src2);
//定义变量
vector<KeyPoint> keypoints1, keypoints2;//定义检测的特征点存储容器
Mat descriptors1,descriptors2;//定义特征点描述信息为Mat类型
Mat result_img;//匹配结果图片
//创建sift特征检测器实例
//将SIFT可以换位SURF、ORB
Ptr<SIFT>detector = SIFT::create();
//提取特征点
detector->detect(src1,keypoints1,noArray());
detector->detect(src2, keypoints2, Mat());
//获取特征点的描述信息=>特征向量
detector->compute(src1,keypoints1,descriptors1);
detector->compute(src2, keypoints2, descriptors2);
//定义匹配器的实例化=>方法为暴力匹配法
Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create(DescriptorMatcher::BRUTEFORCE);//create中的参数可以填string FlannBased等匹配方法
//第二种实例化方法
//BFMatcher matcher;
//进行暴力匹配
vector<DMatch> matches;
//第一个参数为queryDescription为目标,第二个参数为trainDescription模板
matcher->match(descriptors1,descriptors2,matches);
//限制特征点匹配数量=》只匹配前20个较好的特征点
int num = 20;
nth_element(matches.begin(), matches.begin()+num,matches.end());
//vector去除20以后的元素
matches.erase(matches.begin()+num,matches.end());
//输出关键点和匹配结果
//其中右侧图为trainDescription模板,左侧图为queryDescription目标
//左图中的点与右图中进行匹配对应
drawMatches(src1,keypoints1,src2,keypoints2, matches,result_img);
drawKeypoints(src1,keypoints1,src1);
drawKeypoints(src2,keypoints2,src2);
imshow("匹配结果",result_img);
imshow("特征点1",src1);
imshow("特征点2",src2);
waitKey(0);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果: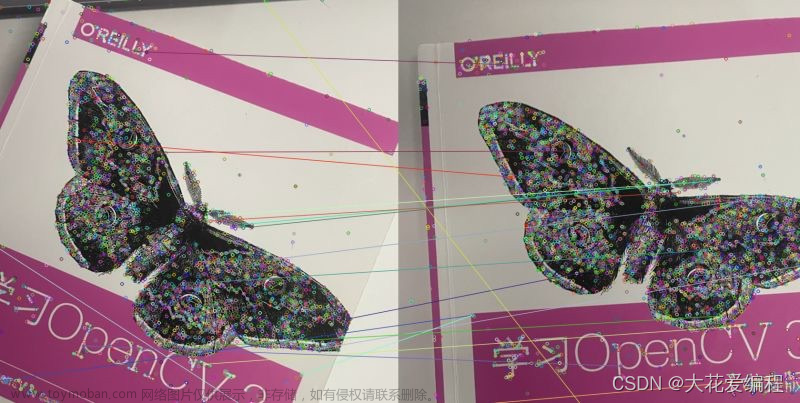
代码2(通过距离进行滤波)
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include<opencv2\highgui\highgui.hpp>
#include<opencv2\imgproc\imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/xfeatures2d.hpp>
using namespace cv; //包含cv命名空间
using namespace std;
using namespace xfeatures2d;
int main() {
system("color 2E");
//载入图片
Mat src1 = imread("E:\\乔大花进度\\11-18\\sift特征检测和匹配\\3.jpg",1);
Mat src2 = imread("E:\\乔大花进度\\11-18\\sift特征检测和匹配\\4.jpg", 1);
//显示原图
imshow("原图1",src1);
imshow("原图2", src2);
//定义变量
vector<KeyPoint> keypoints1, keypoints2;//定义检测的特征点存储容器
Mat descriptors1,descriptors2;//定义特征点描述信息为Mat类型
Mat result_img;//匹配结果图片
//创建sift特征检测器实例
//将SIFT可以换位SURF、ORB
Ptr<SIFT>detector = SIFT::create();
//提取特征点
detector->detect(src1,keypoints1,noArray());
detector->detect(src2, keypoints2, Mat());
//获取特征点的描述信息=>特征向量
detector->compute(src1,keypoints1,descriptors1);
detector->compute(src2, keypoints2, descriptors2);
//定义匹配器的实例化=>方法为暴力匹配法
Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create(DescriptorMatcher::BRUTEFORCE);//create中的参数可以填string FlannBased等匹配方法
//第二种实例化方法
//BFMatcher matcher;
//进行暴力匹配
vector<DMatch> matches;
//第一个参数为queryDescription为目标,第二个参数为trainDescription模板
matcher->match(descriptors1,descriptors2,matches);
//限制特征点匹配数量=》只匹配前20个较好的特征点
int num = 20;
nth_element(matches.begin(), matches.begin()+num,matches.end());
//vector去除20以后的元素
matches.erase(matches.begin()+num,matches.end());
double Max_distance = matches[1].distance;
double Min_distance = matches[1].distance;
vector<DMatch> goodfeatrues;
//根据特征点的距离去筛选
for (int i = 0; i < matches.size(); i++)
{
double dist = matches[i].distance;
if (dist>Max_distance)
{
Max_distance = dist;
}
if (dist<Min_distance)
{
Min_distance = dist;
}
}
cout << "匹配点的最大距离:" << Max_distance << endl;
cout << "匹配点的最小距离:" << Min_distance << endl;
//M为距离阈值,M越大点数越多
double M = 1.3;
for (int i = 0; i < matches.size(); i++)
{
double dist = matches[i].distance;
if (dist<M*Min_distance) {
goodfeatrues.push_back(matches[i]);
}
}
cout << "最终选取特征点的数量为:" << matches.size() << endl;
//输出关键点和匹配结果
//其中右侧图为trainDescription模板,左侧图为queryDescription目标
//左图中的点与右图中进行匹配对应
drawMatches(src1,keypoints1,src2,keypoints2, goodfeatrues,result_img);
drawKeypoints(src1,keypoints1,src1);
drawKeypoints(src2,keypoints2,src2);
imshow("匹配结果",result_img);
imshow("特征点1",src1);
imshow("特征点2",src2);
waitKey(0);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
代码3(通过knnMatch匹配,可以通过对distance设置阈值进行滤波,效果最好)
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include<opencv2\highgui\highgui.hpp>
#include<opencv2\imgproc\imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/xfeatures2d.hpp>
using namespace cv; //包含cv命名空间
using namespace std;
using namespace xfeatures2d;
int main() {
system("color 2E");
//载入图片
Mat src1 = imread("E:\\乔大花进度\\11-18\\sift特征检测和匹配\\3.jpg",1);
Mat src2 = imread("E:\\乔大花进度\\11-18\\sift特征检测和匹配\\4.jpg", 1);
//显示原图
imshow("原图1",src1);
imshow("原图2", src2);
//定义变量
vector<KeyPoint> keypoints1, keypoints2;//定义检测的特征点存储容器
Mat descriptors1,descriptors2;//定义特征点描述信息为Mat类型
Mat result_img;//匹配结果图片
//创建sift特征检测器实例
//将SIFT可以换位SURF、ORB
Ptr<SIFT>detector = SIFT::create();
//提取特征点
detector->detect(src1,keypoints1,noArray());
detector->detect(src2, keypoints2, Mat());
//获取特征点的描述信息=>特征向量
detector->compute(src1,keypoints1,descriptors1);
detector->compute(src2, keypoints2, descriptors2);
//定义匹配器的实例化=>方法为暴力匹配法
Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create(DescriptorMatcher::BRUTEFORCE);//create中的参数可以填string FlannBased等匹配方法
//第二种实例化方法
//BFMatcher matcher;
//进行暴力匹配
vector<DMatch> matches;
vector<Mat>train_desc(1, descriptors2);
matcher->add(train_desc);
matcher->train();
vector<vector<DMatch>> matchpoints;
matcher->knnMatch(descriptors1,matchpoints,2);
vector<DMatch> goodfeatur;
for (int i = 0; i < matchpoints.size(); i++)
{
if (matchpoints[i][0].distance<0.15*matchpoints[i][1].distance)
{
goodfeatur.push_back(matchpoints[i][0]);
}
}
cout << "筛选后的特征点数量为: " << goodfeatur.size() << endl;
//输出关键点和匹配结果
//其中右侧图为trainDescription模板,左侧图为queryDescription目标
//左图中的点与右图中进行匹配对应
drawMatches(src1,keypoints1,src2,keypoints2, goodfeatur,result_img);
drawKeypoints(src1,keypoints1,src1);
drawKeypoints(src2,keypoints2,src2);
namedWindow("匹配结果",WINDOW_NORMAL);
resizeWindow("匹配结果",500,500);
imshow("匹配结果",result_img);
waitKey(0);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果: 文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-647759.html
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-647759.html
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qiaodahua/article/details/127995517文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-647759.html
到了这里,关于opencv学习-特征匹配的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!