使用kociemba模块可以快速地得到3阶魔方的还原步骤,例如:
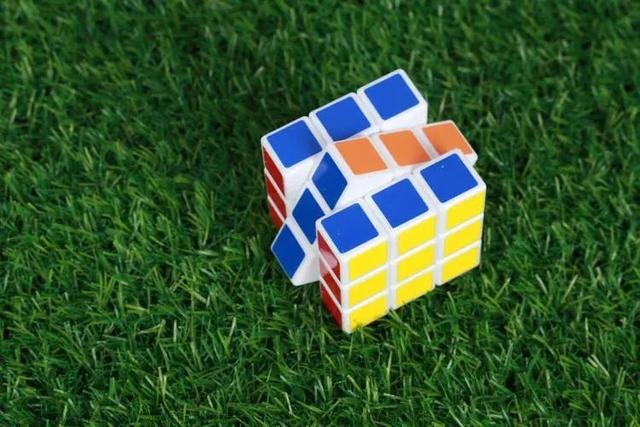

U = '红绿黄白红白白蓝白'
R = '红蓝绿绿绿蓝黄红红'
F = '绿橙绿黄白红蓝橙红'
D = '橙黄绿红橙蓝橙黄黄'
L = '白橙橙绿蓝红白白黄'
B = '橙白蓝黄黄橙蓝绿蓝'
cubdict = {U[4]: 'U', R[4]: 'R', F[4]: 'F', D[4]: 'D', L[4]: 'L', B[4]: 'B'}
UC = ''
for s in [U, R, F, D, L, B]:
for i in range(9):
UC = UC + cubdict[s[i]]
print(UC)
print(kc.solve(UC))
指定面向自己的一面为Front(F),相对的一面即为Back(B),左边的一面为Left(L),右边的一面为Right(R),上面为Up(U),下面为Down(D),将魔方的6个面的颜色分别写到U R F D L B中,最后就会打印出还原魔方所有的步骤,按照步骤操作即可还原。
但是,每次都要自己输颜色会显得自己比较low,所以可以借用opencv的图像处理功能来进行魔方颜色的自动识别,例如:文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-686191.html
import kociemba as kc
import os
import cv2
import numpy as np
from copy import deepcopy
import math
def imgcheck(frame_raw):
hsv_table = [[[0, 10], [43, 255], [46, 255], '红'],
[[156, 180], [43, 255], [46, 255], '红'],
[[11, 20], [43, 255], [46, 255], '橙'],
[[20, 34], [43, 255], [46, 255], '黄'],
[[35, 80], [43, 255], [46, 255], '绿'],
[[80, 99], [43, 255], [46, 255], '青'],
[[100, 124], [43, 255], [46, 255], '蓝'],
[[125, 155], [43, 255], [46, 255], '紫'],
[[0, 180], [0, 30], [166, 255], '白'],
[[0, 180], [0, 43], [46, 166], '灰'],
[[0, 180], [0, 255], [0, 46], '黑']]
cube_list = []
frame = frame_raw.copy()
index = 0
center = []
candidates = []
hsv = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
for process_ind in range(2):
hsv = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
#cv2.imshow("image", hsv)
#cv2.waitKey(0)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
blurred = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (3, 3), 0)
canny = cv2.Canny(blurred, 20, 40)
#cv2.imshow("image", canny)
#cv2.waitKey(0)
if process_ind == 0:
kernel = np.ones((3, 3), np.uint8)
dilated = cv2.dilate(canny, kernel, iterations=12)
else:
kernel = np.ones((6, 6), np.uint8)
dilated = cv2.dilate(canny, kernel, iterations=3)
if process_ind == 1 or process_ind == 0:
cv2.imshow("image", dilated)
cv2.waitKey(0)
(contours, hierarchy) = cv2.findContours(dilated.copy(), cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
hierarchy = hierarchy[0]
pre_cX = 0
pre_cY = 0
area_arr = []
for component in zip(contours, hierarchy):
contour = component[0]
peri = cv2.arcLength(contour, True)
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(contour, 0.1 * peri, True)
area = cv2.contourArea(contour)
corners = len(approx)
# compute the center of the contour
M = cv2.moments(contour)
if M["m00"]:
cX = int(M["m10"] / M["m00"])
cY = int(M["m01"] / M["m00"])
else:
cX = None
cY = None
if cX is not None:
if process_ind == 0:
tmp = {'area': area, 'contour': contour}
area_arr.append(tmp)
elif 60000 > area > 1000:
tmp = {'index': index, 'cx': cX, 'cy': cY, 'contour': contour}
center.append(tmp)
index += 1
if process_ind == 0:
area_arr.sort(key=lambda k: (k.get('area', 0)), reverse=True)
mx,my,mw,mh = cv2.boundingRect(area_arr[0].get('contour'))
cv2.rectangle(frame, (mx,my), (mx+mw, my+mh), (0, 255, 0), 2)
#cv2.imshow("image", frame)
#cv2.waitKey(0)
frame = frame[my-5:my+mh+5, mx-5:mx+mw+5]
#cv2.imshow("image", frame)
#cv2.waitKey(0)
frame = cv2.resize(frame, (320, 320))
#if index < 9:
# return
print(str(index))
'''
center.sort(key=lambda k: (k.get('cx', 0)))
center.sort(key=lambda k: (k.get('cy', 0)))
'''
center.sort(key=lambda k: (k.get('cy', 0)))
row1 = center[0:3]
row1.sort(key=lambda k: (k.get('cx', 0)))
row2 = center[3:6]
row2.sort(key=lambda k: (k.get('cx', 0)))
row3 = center[6:9]
row3.sort(key=lambda k: (k.get('cx', 0)))
center.clear()
center = row1 + row2 + row3
for component in center:
candidates.append(component.get('contour'))
x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(component.get('contour'))
if abs(w - h) < 10:
cv2.rectangle(frame, (x, y), (x+w, y+h), (0, 255, 0), 2)
#cv2.imshow("image", frame)
#cv2.waitKey(0)
h_ = 0
s_ = 0
v_ = 0
ss = w * h
for i in range(w):
for j in range(h):
h_ = h_ + hsv[y+j][x+i][0]
s_ = s_ + hsv[y+j][x+i][1]
v_ = v_ + hsv[y+j][x+i][2]
h_ = h_ / ss
s_ = s_ / ss
v_ = v_ / ss
print(str(h_) + ',' + str(s_) + ',' + str(v_))
for k in hsv_table:
if k[0][0] < h_ < k[0][1] and k[1][0] < s_ < k[1][1] and k[2][0] < v_ < k[2][1]:
# print(k[3])
cube_list.append(k[3])
break
print(str(len(cube_list)))
#if len(cube_list) == 9:
print(cube_list)
#cv2.drawContours(frame, candidates, -1, (0, 0, 255), 3)
cv2.imshow("image", frame)
cv2.waitKey(0)
if __name__ == "__main__":
webcam = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
if not webcam.isOpened():
print("can't open the camera!!!")
while True:
ret, frame = webcam.read()
rec_w = 200
rec_h = 200
rec_y = int((frame.shape[0] - rec_h)/2)
rec_x = int((frame.shape[1] - rec_w) / 2)
cv2.rectangle(frame, (rec_x, rec_y), (rec_x + rec_w, rec_y + rec_h), (0, 255, 0), 2)
imgcheck(frame)
cv2.imshow("video", frame)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
webcam.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
hsv_table的各个颜色的范围可能需要根据实际情况进行调试。文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-686191.html
到了这里,关于基于Python+kociemba+opencv的3阶魔方自动还原的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!