一、要求
1.采用高级语言编写程序模拟文件系统,文件系统采用多级目录结构,实现对文件和目录的创建、删除、重命名、变更权限、显示文件内容、修改文件内容等操作。
2.撰写课程设计报告。
二、课程设计内容
编写程序模拟一个简单的文件系统,具体实验内容如下:
(1)实现多级目录结构,而非二级目录结构。
(2)实现文件和目录的创建、删除、重命名和读写权限控制功能。
(3)实现显示文件内容和更改文件内容的功能。
(4)创建文件或目录时,采用动态申请的方式请求存储空间分配,在删除文件或目录时,还需对申请的空间进行释放。
(5)为观察各种命令执行情况,要求以树形结构直观地显示命令执行后的目录结构。
主要数据结构说明
//用户的结构体
typedef struct USER
{
char name[100]; //用户名
int userRights; //用户权限 0可编辑文件权限、1为可读可写可删除、2为可读不可写不可删除 、3为不可读不可写不可删除
char account[256]; //用户账号
char password[256]; //用户密码
int state; //登录状态
}USER;
//文件的结构体
typedef struct
{
char name[FILENAME_MAX]; //文件名
char content[FILELEN]; //文件内容
struct FILES* frontFile; //同级目录上一文件
struct FILES* nextFile; //同级目录下一文件
struct FOLDERS* parentFolder; //父目录
int canRead; //是否可读
int canWrite; //是否可写
} FILES;
//目录的结构体
typedef struct
{
char name[256]; //目录名
struct FOLDERS* nextFolder; //同级下一目录
struct FOLDERS* frontFolder; //同级上一目录
struct FOLDERS* parentFolder; //父目录
struct FOLDERS* firstChildFolder; //子目录
struct FILES* firstChildFile; //首个子文件
struct FILES* lastChildFile; //最后一个子文件
int canRead; //是否可读
int canWrite; //是否可写
}FOLDERS;
在模拟程序中,应先建立文件系统的根目录,文件系统中的操作都在此目录下完成,且不得直接对根目录操作。
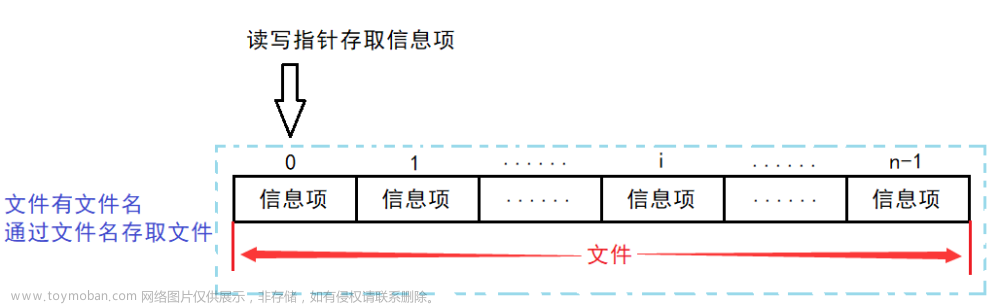
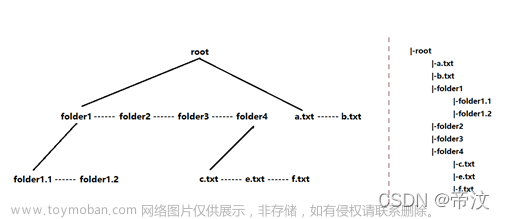
在指定目录下新建立的文件和目录,都通过该目录中最后一个子文件或子目录的nextFile或nextFolder指针建立连接;若该目录之中无任何子文件和子目录,则通过该目录的firstChildFolder或firstChildFile指针建立连接。如图所示。
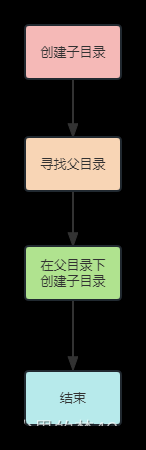
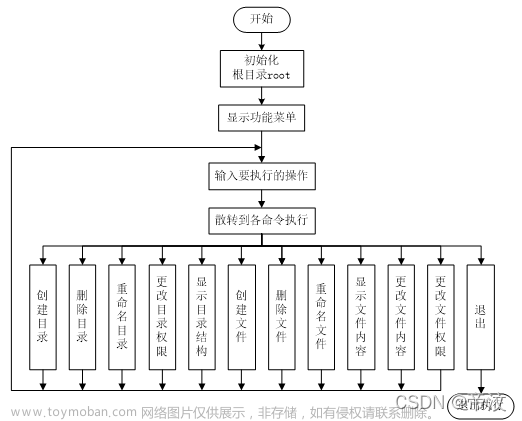
文件系统模拟程序执行流程
(1)程序运行时,系统首先根据目录FOLDER结构建立根目录root,并为其分配空间,初始化其信息。
(2)程序给出一个菜单,用户根据菜单选项前的数字,选择要执行的操作命令。
(3)若在根目录下建立子目录,则建立一个新FOLDER并为其分配空间后,利用根目录中的子目录节点指针与该子目录建立连接。
(4)若在根目录下建立文件,则建立一个新FCB并为其分配空间后,利用根目录中的子文件节点指针与该文件建立连接。
(5)对指定文件或目录进行删除、重命名、设置权限等操作时,需要先在文件系统中找到目标文件或目录才可进行下一步的操作,否则提示用户目标文件或目录不存在。
(6)若文件或目录若不具有可读权限,不会在文件系统中显示,处于隐藏状态,但并不代表不存在;文件或目录若不具有可写权限,则不能对在该目录下执行创建,删除,不能重命名该目录;不能更改文件内容。
(7)每次执行操作命令后,为直观地观察执行情况,会显示输出命令执行后的目录结构。
文件系统执行流程如图所示。
编译器:CodeBlocks 20.03
c语言标准:c11
代码
主函数以及各定义
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#define FILENAME_MAX 256
#define FOLDERNAME_MAX 256
#define FILELEN 1000
//用户的结构体
typedef struct USER
{
char name[100]; //用户名
int userRights; //用户权限 0为最高级权限,3为最低级权限
char account[256]; //用户账号
char password[256]; //用户密码
int state; //登录状态
}USER;
//文件的结构体
typedef struct
{
char name[FILENAME_MAX]; //文件名
char content[FILELEN]; //文件内容
struct FILES* frontFile; //同级目录上一文件
struct FILES* nextFile; //同级目录下一文件
struct FOLDERS* parentFolder; //父目录
int canRead; //是否可读
int canWrite; //是否可写
} FILES;
//目录的结构体
typedef struct
{
char name[FOLDERNAME_MAX]; //目录名
struct FOLDERS* nextFolder; //同级下一目录
struct FOLDERS* frontFolder; //同级上一目录
struct FOLDERS* parentFolder; //父目录
struct FOLDERS* firstChildFolder; //子目录
struct FILES* firstChildFile; //首个子文件
struct FILES* lastChildFile; //最后一个子文件
int canRead; //是否可读
int canWrite; //是否可写
}FOLDERS;
int login();//登录函数
struct USER QueryUser(account,pwd);//用户表
void getPath(FOLDERS* nowPath);//获取当前文件夹路径
void getAllFolder(FOLDERS* nowFOLDER, int userRights);//显示当前目录下所有文件夹
void getAllFile(FOLDERS* nowFOLDER, int useRights);//进入文件
void modifyFolder(FOLDERS* handFFOLDER, int userRights);//修改目录
void modifyFile(FILES *handFFILE,int userRights);//修改文件
void backParFolder(FOLDERS *nowFOLDER);//返回父目录
void OperateFolder(FOLDERS* nowFOLDER, int userRights);//操作当前目录下文件夹
void OperateFile(FOLDERS *nowFOLDER,int userRights);//操作当前文件
void CreatRootFolder(FOLDERS* rootFolder);//创建根目录
int main()
{
FOLDERS* LF, * nowFolder,*parFolder;
LF = (FOLDERS*)malloc(sizeof(FOLDERS));
nowFolder = (FOLDERS*)malloc(sizeof(FOLDERS));
parFolder = (FOLDERS*)malloc(sizeof(FOLDERS));
parFolder=NULL;
CreatRootFolder(LF);//创建根目录
nowFolder = LF;
int Choice = 0;
int userRights = 0;
userRights = login();
while (1)
{
printf("------------------------------------\n\n");
getPath(nowFolder);
printf("1.查看当前目录下内容\n");
printf("2.返回父目录\n");
printf("3.在当前目录下操作文件夹\n");
printf("4.在当前目录下操作文件\n");
printf("5.退出系统\n");
printf("请输入要进行的操作序号:");
scanf("%d", &Choice);
switch (Choice) {
case 1:
getAllFolder(nowFolder, userRights);
getAllFile(nowFolder, userRights);
break;
case 2:
backParFolder(nowFolder);
break;
case 3:
OperateFolder(nowFolder, userRights);
break;
case 4:
OperateFile(nowFolder, userRights);
break;
case 5:
userRights = login();
break;
}
Choice = 0;
}
}
登录函数
int login()
{
char account[256];
char pwd[256];
printf("----------登录文件查询系统----------\n");
printf("账号:");
scanf("%s", account);
printf("密码:");
scanf("%s", pwd);
printf("------------------------------------\n");
USER user = QueryUser(&account, &pwd);
if(user.state==0)
{
printf("登录失败!\n");
login();
}
else
{
printf("用户权限:%d\n", user.userRights);
return user.userRights;
}
}
用户信息查询函数
struct USER QueryUser(char account[256], char pwd[256])//查询用户信息
{
struct USER userlist[10] = {
{"admin",0,"admin","admin",0},
{"user1",1,"user1","123456",0},
{"user2",2,"user2","123456",0},
{"user3",3,"user3","123456",0},
{"user4",2,"user4","12345678",0}
};
struct USER FailUser = { "登陆失败",3,"登陆失败","登陆失败",0 };
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
if (strcmp(account, userlist[i].account) == 0)
{
if (strcmp(pwd, userlist[i].password) == 0)
{
userlist[i].state = 1;
printf("登陆成功!欢迎你%s!\n", userlist[i].name);
return userlist[i];
}
else printf("密码错误!\n");
return FailUser;
}
}
printf("账号不存在!\n");
return FailUser;
}
获取当前所在目录路径
void getPath(FOLDERS *nowFOLDER)
{
FOLDERS* handFOLDER;
handFOLDER = (FOLDERS*)malloc(sizeof(FOLDERS));
handFOLDER = nowFOLDER;
char nowPath[1000], tempPath[1000]="/", a[1000]="";
strcpy(nowPath, strcat(tempPath, handFOLDER->name));
while (1)
{
memset(a,'\0',sizeof(a));
a[0]='/';
if (handFOLDER->parentFolder != NULL)
{
handFOLDER = handFOLDER->parentFolder;
strcat(a,handFOLDER->name);
strcat(a,nowPath );
strcpy(nowPath,a);
}
else
{
printf("当前位置:%s\n", nowPath);
break;
}
}
}
创建根目录
void CreatRootFolder(FOLDERS* rootFolder) {
FOLDERS* r = rootFolder;
strcpy(r->name, "root");
r->nextFolder = NULL;
r->frontFolder = NULL;
r->firstChildFolder = NULL;
r->firstChildFile = NULL;
r->parentFolder = NULL;
r->lastChildFile = NULL;
r->canRead = 3;
r->canWrite = 0;
printf("创建根目录%s成功!\n", r->name);
}
获取当前目录下所有子目录信息
void getAllFolder(FOLDERS* nowFOLDER, int userRights) {
if(nowFOLDER->canRead < userRights)
{
printf("权限不足无法读取该目录!\n");
return 0;
}
else
{
FOLDERS* handFOLDER;//当前遍历到的目录
handFOLDER = (FOLDERS*)malloc(sizeof(FOLDERS));
handFOLDER = nowFOLDER;
if (handFOLDER->firstChildFolder == NULL)
{
printf("当前目录下无子目录\n");
}
else
{
printf("当前目录下的子目录列表:\n");
handFOLDER = handFOLDER->firstChildFolder;
printf("/%s\n", handFOLDER->name);
while (1)
{
handFOLDER = handFOLDER->nextFolder;
if (handFOLDER->name == NULL)
{
break;
}
else
{
printf("/%s\n", handFOLDER->name);
}
}
}
}
}
获取当前目录下所有文件信息
void getAllFile(FOLDERS* nowFOLDER, int useRights) {
if (nowFOLDER->firstChildFile != NULL)
{
printf("当前目录下子文件列表:\n");
FILES* handFile;
handFile = (FILES*)malloc(sizeof(FILES));
handFile = nowFOLDER->firstChildFile;
printf("%s\n", handFile->name);
while (1)
{
if (handFile->nextFile == NULL)
break;
else
{
handFile = handFile->nextFile;
printf("%s\n", handFile->name);
}
}
}
else
printf("该目录下无文件!\n");
}
对单个目录或文件进行修改
void modifyFolder(FOLDERS *modifyFOLDER, int userRights)
{
printf("当前目录信息:\n");
printf("目录名:%s\n", modifyFOLDER->name);
printf("可读权限:%d\n", modifyFOLDER->canRead);
printf("可写权限:%d\n", modifyFOLDER->canWrite);
while (1)
{
int Choice = 0;
printf("------------------------------------\n\n");
printf("1.文件名\n");
printf("2.可读权限\n");
printf("3.可写权限\n");
printf("4.退出修改\n");
printf("请输入要修改的选项:");
scanf("%d", &Choice);
if (Choice == 1)
{
int flag = 0;
char name[256];
FOLDERS* handFOLDER;
handFOLDER = (FOLDERS*)malloc(sizeof(FOLDERS));
handFOLDER = modifyFOLDER;
printf("请输入新的目录名:");
scanf("%s,", name);
while (1)
{
if (handFOLDER->frontFolder != NULL)
{
handFOLDER = handFOLDER->frontFolder;
if (strcmp(handFOLDER->name, name) && strlen(handFOLDER->name) == strlen(name))
{
printf("该目录名已存在!\n");
flag = 1;
break;
}
}
else
flag = 0;
break;
}
while (1)
{
if (handFOLDER->nextFolder != NULL && flag == 0)
{
handFOLDER = handFOLDER->nextFolder;
if (strcmp(handFOLDER->name, name) && strlen(handFOLDER->name) == strlen(name))
{
printf("该目录名已存在!\n");
flag = 1;
break;
}
}
else
flag = 0;
break;
}
if (flag == 0)
{
strcpy(modifyFOLDER->name, name);
printf("修改目录名成功!\n");
}
}
if (Choice == 2)
{
int read = 3;
printf("请输入可读权限:");
scanf("%d", &read);
if (read < userRights)
printf("无法修改为更高权限!\n");
else if (read > 3)
printf("无法修改为低于3的权限!\n");
else
{
modifyFOLDER->canRead = NULL;
modifyFOLDER->canRead = read;
printf("修改可读权限成功!\n");
}
}
if (Choice == 3)
{
int write = 3;
printf("请输入可写权限:");
scanf("%d", &write);
if (write < userRights)
printf("无法修改为更高权限!\n");
else if (write > 3)
printf("无法修改为低于3的权限!\n");
else
{
modifyFOLDER->canWrite = NULL;
modifyFOLDER->canWrite = write;
printf("修改可写权限成功!\n");
}
}
if (Choice == 4)
break;
}
}
void modifyFile(FILES *modifyFILE,int userRights){
if(userRights>modifyFILE->canWrite)
{
printf("用户权限不足无法修改该文件!\n");
return 0;
}
else
{
while(1)
{
int Choice=0;
printf("1.文件名\n");
printf("2.可读权限\n");
printf("3.可写权限\n");
printf("4.修改文件内容\n");
printf("5.退出修改\n");
printf("请输入要修改项:");
scanf("%d",&Choice);
FILES *handFILE;
handFILE = (FILES*)malloc(sizeof(FILES));
handFILE = modifyFILE;
if(Choice==1)
{
int flag=0;
char name[256]="";
printf("请输入文件名:");
scanf("%s",name);
while(1)
{
if(handFILE->frontFile!=NULL&&flag==0)
{
handFILE=handFILE->frontFile;
if(strcmp(handFILE->name,name) == 0 && strlen(handFILE->name) == strlen(name))
flag=1;
}
else if(flag==1)
{
printf("1该目录下已存在该文件!\n");
break;
}
else if(handFILE->frontFile==NULL&&flag==0)
break;
}
if(flag==0)
{
while(1)
{
if(handFILE->nextFile!=NULL&&flag==0)
{
handFILE=handFILE->nextFile;
if(strcmp(handFILE->name,name) == 0 && strlen(handFILE->name) == strlen(name))
flag=1;
}
else if(flag==1)
{
printf("2该目录下已存在该文件!\n");
break;
}
else if(handFILE->nextFile==NULL&&flag==0)
break;
}
}
if(flag==0)
{
strcpy(modifyFILE->name,name);
printf("修改文件名成功!\n");
}
}
if(Choice==2)
{
int read=0;
printf("请输入可读权限:");
scanf("%d",&read);
if(read<userRights)
printf("修改的权限大于了用户权限,修改失败!\n");
else if(read>3)
printf("修改的权限不可大于3,修改失败!\n");
else
{
modifyFILE->canRead=read;
printf("修改成功!\n");
}
}
if(Choice==3)
{
int write=0;
printf("请输入可读权限:");
scanf("%d",&write);
if(write<userRights)
printf("修改的权限大于了用户权限,修改失败!\n");
else if(write>3)
printf("修改的权限不可大于3,修改失败!\n");
else
{
modifyFILE->canWrite=write;
printf("修改成功!\n");
}
}
if(Choice==4)
{
strcpy(modifyFILE->content,"");
printf("请输入文件内容以 #! 作为结束符:\n");
int fileslen = 0;
char ch;
while ((ch = getchar()))
{
if (ch == '!' && modifyFILE->content[fileslen - 1] == '#')
{
modifyFILE->content[fileslen] = ch;
break;
}
else
{
modifyFILE->content[fileslen] = ch;
fileslen++;
}
}
printf("修改文件内容成功!\n");
}
if(Choice==5)
return 0;
}
}
}
返回父目录
void backParFolder(FOLDERS *nowFOLDER){
if(nowFOLDER->parentFolder!=NULL)
{
FOLDERS *parFOLDER;
parFOLDER = (FOLDERS*)malloc(sizeof(FOLDERS));
parFOLDER = nowFOLDER->parentFolder;
*nowFOLDER = *parFOLDER;
}
else
printf("无父目录!\n");
return 0;
}
在当前目录下操作文件夹
void OperateFolder(FOLDERS* nowFOLDER, int userRights) {
int Choice;
printf("------------------------------------\n\n");
printf("1.进入子目录\n");
printf("2.创建子目录\n");
printf("3.删除子目录\n");
printf("4.修改子目录\n");
printf("5.返回目录操作项\n");
printf("请选择要操作的序列号:");
scanf("%d", &Choice);
printf("------------------------------------\n\n");
if (Choice == 1)
{
char name[100];
printf("请输入要进入的子目录:");
scanf("%s", name);
FOLDERS* handFFOLDER;
handFFOLDER = (FOLDERS*)malloc(sizeof(FOLDERS));
handFFOLDER = nowFOLDER;
if (handFFOLDER->firstChildFolder != NULL)
{
handFFOLDER = handFFOLDER->firstChildFolder;
if (strcmp(handFFOLDER->name, name) == 0 && strlen(name) == strlen(handFFOLDER->name))
{
if(userRights<handFFOLDER->canRead)
{
printf("handFFOLDER:%s\n", handFFOLDER->name);
printf("handFFOLDERparent:%s\n", handFFOLDER->parentFolder);
printf("nowfolder:%s\n",nowFOLDER->name);
FOLDERS *parFOLDER;
parFOLDER=(FOLDERS *)malloc(sizeof (FOLDERS));
strcpy(parFOLDER->name,nowFOLDER->name);
parFOLDER->canRead=nowFOLDER->canRead;
parFOLDER->canWrite=nowFOLDER->canWrite;
parFOLDER->firstChildFile=nowFOLDER->firstChildFile;
parFOLDER->firstChildFolder=nowFOLDER->firstChildFolder;
parFOLDER->nextFolder=nowFOLDER->nextFolder;
parFOLDER->parentFolder=nowFOLDER->parentFolder;
parFOLDER->frontFolder=nowFOLDER->frontFolder;
parFOLDER->lastChildFile=parFOLDER->lastChildFile;
*nowFOLDER=*handFFOLDER ;
nowFOLDER->parentFolder=parFOLDER;
return 0;
}
else
{
printf("用户权限不足无法进入!\n");
return 0
}
}
else
{
if (handFFOLDER->nextFolder != NULL)
{
handFFOLDER = handFFOLDER->nextFolder;
while (1)
{
if (handFFOLDER != NULL)
{
if (strcmp(handFFOLDER->name, name) == 0 && strlen(name) == strlen(handFFOLDER->name))
{
if(userRights<handFFOLDER->canRead)
{
FOLDERS *parFOLDER;
parFOLDER=(FOLDERS *)malloc(sizeof (FOLDERS));
strcpy(parFOLDER->name,nowFOLDER->name);
parFOLDER->canRead=nowFOLDER->canRead;
parFOLDER->canWrite=nowFOLDER->canWrite;
parFOLDER->firstChildFile=nowFOLDER->firstChildFile;
parFOLDER->firstChildFolder=nowFOLDER->firstChildFolder;
parFOLDER->nextFolder=nowFOLDER->nextFolder;
parFOLDER->parentFolder=nowFOLDER->parentFolder;
parFOLDER->frontFolder=nowFOLDER->frontFolder;
parFOLDER->lastChildFile=parFOLDER->lastChildFile;
*nowFOLDER=*handFFOLDER;
nowFOLDER->parentFolder=parFOLDER;
return 0;
}
else
{
printf("用户权限不足无法进入!\n");
return 0
}
}
else
{
handFFOLDER = handFFOLDER->nextFolder;
}
}
else
break;
}
}
}
printf("该文件夹不存在!\n");
return 0;
}
else
{
printf("当前目录下文件夹为空!\n");
return 0;
}
getAllFolder(handFFOLDER, userRights);
}
else if (Choice == 2)
{
FOLDERS* newFOLDER, * handFOLDER;//新的文件夹,目前文件夹
newFOLDER = (FOLDERS*)malloc(sizeof(FOLDERS));
handFOLDER = (FOLDERS*)malloc(sizeof(FOLDERS));
handFOLDER = nowFOLDER;
char name[100];
printf("请输入要创建目录的名称:");
scanf("%s", newFOLDER->name);
newFOLDER->nextFolder = NULL;
newFOLDER->firstChildFile = NULL;
newFOLDER->firstChildFolder = NULL;
newFOLDER->parentFolder = handFOLDER;
newFOLDER->canRead = userRights;
newFOLDER->canWrite = userRights;
newFOLDER->lastChildFile = NULL;
if (handFOLDER->firstChildFolder == NULL)
{
handFOLDER->firstChildFolder = newFOLDER;
}
else
{
handFOLDER = handFOLDER->firstChildFolder;
while (1)
{
if (strcmp(handFOLDER->name, newFOLDER->name) == 0 && strlen(handFOLDER->name) == strlen(newFOLDER->name))
{
printf("该目录已存在,请修改名称后创建!\n");
return 0;
}
if (handFOLDER->nextFolder != NULL)
handFOLDER = handFOLDER->nextFolder;
else
{
handFOLDER->nextFolder = newFOLDER;
newFOLDER->frontFolder = handFOLDER;
break;
}
}
}
printf("创建新文件夹成功!\n");
getAllFolder(nowFOLDER, userRights);
return 0;
}
if (Choice == 3)
{
char name[100];
printf("请输入要删除的子目录:");
scanf("%s", name);
FOLDERS* handFFOLDER, * handnext;
handFFOLDER = (FOLDERS*)malloc(sizeof(FOLDERS));
handnext = (FOLDERS*)malloc(sizeof(FOLDERS));
handFFOLDER = nowFOLDER;
if (handFFOLDER->firstChildFolder != NULL)
{
handFFOLDER = handFFOLDER->firstChildFolder;
if (strcmp(handFFOLDER->name, name) == 0 && strlen(handFFOLDER->name) == strlen(name))
{
if(userRights>handFFOLDER->canWrite)
{
printf("权限不足无法删除!\n");
return 0;
}
else
{
if (handFFOLDER->nextFolder == NULL)
nowFOLDER->firstChildFolder = NULL;
else
{
handFFOLDER = handFFOLDER->nextFolder;
nowFOLDER->firstChildFolder = handFFOLDER;
handFFOLDER->frontFolder = NULL;
}
printf("删除目录成功!\n");
return 0;
}
}
else
{
while (1)
{
handFFOLDER = handFFOLDER->nextFolder;
if (strcmp(handFFOLDER->name, name) == 0 && strlen(handFFOLDER->name) == strlen(name))
{
if (handFFOLDER->nextFolder == NULL)
{
if(userRights>handFFOLDER->canWrite)
{
printf("权限不足无法删除!\n");
return 0;
}
else
{
handFFOLDER = handFFOLDER->frontFolder;
handFFOLDER->nextFolder = NULL;
printf("删除目录成功!\n");
return 0;
}
}
else
{
if(userRights>handFFOLDER->canWrite)
{
printf("权限不足无法删除!\n");
return 0;
}
else
{
handnext = handFFOLDER->nextFolder;
handFFOLDER = handFFOLDER->frontFolder;
handFFOLDER->nextFolder = handnext;
handnext->frontFolder = handFFOLDER;
printf("删除目录成功!\n");
return 0;
}
}
}
if (handFFOLDER->nextFolder == NULL)
{
printf("该目录不存在!\n");
return 0;
}
}
}
}
printf("该目录下无子目录!\n");
return 0;
}
if (Choice == 4)
{
char name[100];
printf("请输入要修改的子目录:");
scanf("%s", name);
FOLDERS* handFFOLDER;
handFFOLDER = (FOLDERS*)malloc(sizeof(FOLDERS));
handFFOLDER = nowFOLDER;
if (handFFOLDER->firstChildFolder != NULL)
{
handFFOLDER = handFFOLDER->firstChildFolder;
if (strcmp(handFFOLDER->name, name) == 0 && strlen(handFFOLDER->name) == strlen(name))
{
printf("userr:%d\n", userRights);
if (handFFOLDER->canWrite < userRights)
printf("用户权限不足无法修改!\n");
else
modifyFolder(handFFOLDER, userRights);
return 0;
}
else
{
while (1)
{
if (handFFOLDER->nextFolder != NULL)
{
handFFOLDER = handFFOLDER->nextFolder;
if (strcmp(handFFOLDER->name,name) == 0 && strlen(handFFOLDER->name) == strlen(name))
{
if (handFFOLDER->canWrite < userRights)
printf("用户权限不足无法修改!\n");
else
{
modifyFolder(handFFOLDER, userRights);
}
return 0;
}
}
else
{
printf("该目录不存在!\n");
return 0;
}
}
}
}
else
{
printf("该目录不存在!\n");
return 0;
}
}
}
在当前目录下操作文件文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-810244.html
void OperateFile(FOLDERS* nowFolder, int userRights) {
int Choice;
printf("------------------------------------\n\n");
printf("1.查看子文件\n");
printf("2.创建子文件\n");
printf("3.删除子文件\n");
printf("4.修改子文件\n");
printf("5.返回目录操作项\n");
printf("请选择要操作的序列号:");
scanf("%d", &Choice);
printf("------------------------------------\n\n");
if (Choice == 1)
{
if (nowFolder->firstChildFile != NULL)
{
char name[256];
printf("请输入要查看的文件名:");
scanf("%s", name);
FILES* handFFile;
handFFile = (FILES*)malloc(sizeof(FILES));
handFFile = nowFolder->firstChildFile;
while (1)
{
if (strcmp(handFFile, name) == 0 && strlen(handFFile->name) == strlen(name))
{
if (handFFile->canRead < userRights)
{
printf("用户权限不足无法读取该文件!\n");
return 0;
}
else
{
printf("文件可读权限:%d\n", handFFile->canRead);
printf("文件可写权限:%d\n", handFFile->canWrite);
printf("文件内容:\n");
int clen = 0;
while (1)
{
if (handFFile->content[clen] == '#' && handFFile->content[clen + 1] == '!')
break;
else
{
printf("%c", handFFile->content[clen]);
clen++;
}
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
}
else
{
if (handFFile->nextFile != NULL)
handFFile = handFFile->nextFile;
else
{
printf("该目录不存在该文件!\n");
break;
}
}
}
}
else
printf("该目录下无文件夹!\n");
}
else if (Choice == 2)
{
FILES* newFile, * handFile;
handFile = (FILES*)malloc(sizeof(FILES));
newFile = (FILES*)malloc(sizeof(FILES));
newFile->parentFolder = nowFolder;
newFile->nextFile = NULL;
newFile->frontFile = NULL;
newFile->canRead = userRights;
newFile->canWrite = userRights;
printf("请输入文件名:");
scanf("%s", newFile->name);
if (nowFolder->firstChildFile == NULL)
{
nowFolder->firstChildFile = newFile;
nowFolder->lastChildFile = newFile;
}
else
{
handFile = nowFolder->firstChildFile;
while (1)
{
if (strcmp(handFile->name, newFile->name) == 0 && strlen(handFile->name) == strlen(newFile->name))
{
printf("该文件已存在,请更改文件名!\n");
return 0;
}
if (handFile->nextFile == NULL)
{
handFile->nextFile = newFile;
newFile->frontFile = handFile;
nowFolder->lastChildFile = newFile;
break;
}
else
handFile = handFile->nextFile;
}
}
printf("请输入文件内容以 #! 作为结束符:\n");
int fileslen = 0;
char ch;
while ((ch = getchar()))
{
if (ch == '!' && newFile->content[fileslen - 1] == '#')
{
newFile->content[fileslen] = ch;
break;
}
else
{
newFile->content[fileslen] = ch;
fileslen++;
}
}
printf("创建新文件%s成功!\n", newFile->name);
return 0;
}
else if (Choice == 3)
{
if(nowFolder->firstChildFile!=NULL)
{
FILES *handFFILE;
handFFILE = (FILES*)malloc(sizeof(FILES));
handFFILE=nowFolder->firstChildFile;
char name[256];
printf("请输入要删除的文件名:");
scanf("%s",name);
if(strcmp(handFFILE->name,name)==0&&strlen(handFFILE->name)==strlen(name))
{
if(userRights>handFFILE->canWrite)
{
printf("权限不足无法删除!\n");
return 0;
}
else
{
if(handFFILE->nextFile==NULL)
{
nowFolder->firstChildFile=NULL;
handFFILE->parentFolder=NULL;
}
else
{
handFFILE->parentFolder=NULL;
handFFILE=handFFILE->nextFile;
nowFolder->firstChildFile=handFFILE;
handFFILE->frontFile=NULL;
}
printf("删除文件成功!\n");
return 0;
}
}
if(handFFILE->nextFile!=NULL)
{
while(1)
{
handFFILE=handFFILE->nextFile;
if(strcmp(handFFILE->name,name)==0&&strlen(handFFILE->name)==strlen(name))
{
if(userRights>handFFILE->canWrite)
{
printf("权限不足无法删除!\n");
return 0;
}
else
{
if(handFFILE->nextFile==NULL)
{
handFFILE=handFFILE->frontFile;
handFFILE->nextFile=NULL;
}
else
{
FILES *handnext;
handnext = (FILES*)malloc(sizeof(FILES));
handnext=handFFILE->nextFile;
handFFILE=handFFILE->frontFile;
handFFILE->nextFile=handnext;
handnext->frontFile=handFFILE;
}
printf("删除文件成功!\n");
return 0;
}
}
if(handFFILE->nextFile==NULL)
{
printf("该文件不存在!\n");
return 0;
}
}
}
}
else
printf("该目录下不存在文件!\n");
return 0;
}
else if (Choice == 4)
{
if(nowFolder->firstChildFile!=NULL)
{
FILES *handFFILE;
handFFILE = (FILES*)malloc(sizeof(FILES));
handFFILE=nowFolder->firstChildFile;
char name[256];
printf("请输入要修改的文件名:");
scanf("%s",name);
if(strcmp(handFFILE->name,name)==0&&strlen(handFFILE->name)==strlen(name))
{
modifyFile(handFFILE,userRights);
return 0;
}
if(handFFILE->nextFile!=NULL)
{
while(1)
{
handFFILE=handFFILE->nextFile;
if(strcmp(handFFILE->name,name)==0&&strlen(handFFILE->name)==strlen(name))
{
modifyFile(handFFILE,userRights);
return 0;
}
if(handFFILE->nextFile==NULL)
{
printf("该文件不存在!\n");
return 0;
}
}
}
}
else
printf("该目录下不存在文件!\n");
return 0;
}
else if (Choice == 5)
return 0;
}
以上是本人编写的操作系统课程设计大致内容,程序设计本身还可能存在某些漏洞,欢迎各位大佬指出。文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-810244.html
到了这里,关于操作系统课程设计----模拟文件管理系统(c语言)的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!